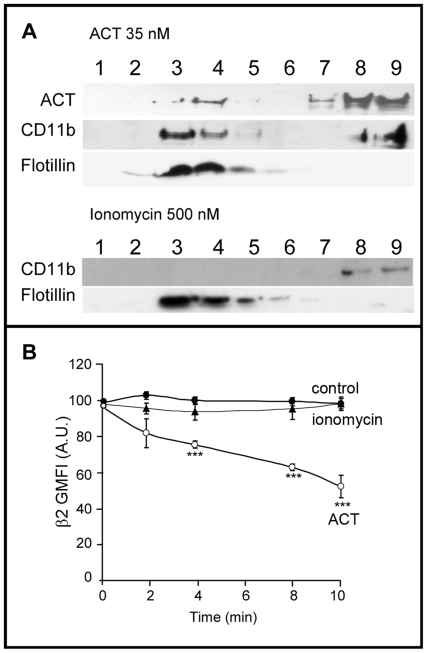
Figure 4. Endocytosis of the CD11b/CD18 integrin depends on ACT-receptor interaction and on ACT-induced calcium influx.
Western blot of the fractions of a sucrose-density gradient stained with an anti-β2 integrin monoclonal antibody and with an anti-ACT monoclonal antibody, for ACT-treated cells (35 nM toxin) and for cells pre-incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C with 500 µM ionomycin before toxin addition. Flotillin, a raft marker protein, was used as control in membrane fractionation and gradient fraction analysis (A). Surface staining of -β2 integrin in control cells [•], ACT-treated cells (35 nM toxin) [○] and ionomycin-treated cells (500 µM ionomycin) [▴] (B). Membrane fractionation by sucrose gradient, analysis by immunoblotting and FACS were performed as described in Materials and Methods. The data shown in (A) are representative of a set of three independent experiments and the data shown in (B) are the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments, with ***p<0.001 with respect to control cells.