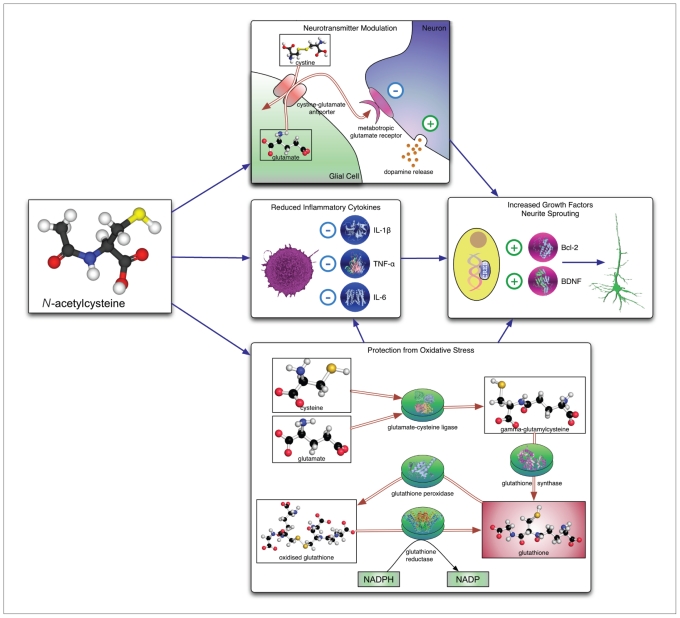
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of action of N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Top to bottom: increased activity of cystine–glutamate antiporter results in increased activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors on inhibitory neurons and facilitates vesicular dopamine release; NAC is associated with reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines and acts as a substrate for glutathione synthesis. These actions are believed to converge upon mechanisms promoting cell survival and growth factor synthesis, leading to increased neurite sprouting. BDNF = brain-derived neurotrophic factor; IL = interleukin; NADP = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH = reduced form of NADP; TNF = tumour necrosis factor.