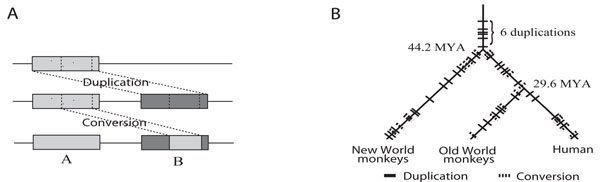
Figure 1.
Depiction of a conversion event and an example of simulation. (A) Depiction of a conversion event. First, a duplication copies region A to B, and A and B begin to diverge through substitutions and other small-scale events. Second, part of B is overwritten by its homologous segment from A in a conversion event. As a result, the converted segment becomes more similar than the other parts of A and B. (B) An example of simulation, with three sequences that mimic those of New World monkeys (NWM), Old World monkeys (OWM), and humans. NWM split from the human lineage 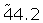 million years ago (MYA), and have about 89% DNA sequence similarity with human.OWM separated
million years ago (MYA), and have about 89% DNA sequence similarity with human.OWM separated 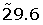 MYA, with about 93% similarity to the human sequence. Randomly applied substitutions simulate the divergence rates among these three clades, starting from an ancestral sequence (see main text). The bold and dotted lines represent duplication and conversion events, respectively, and the location of each line indicates the time of the event. In this example, the simulated human lineage has a total of 18 duplication and 8 conversion events from the starting ancestral sequence.
MYA, with about 93% similarity to the human sequence. Randomly applied substitutions simulate the divergence rates among these three clades, starting from an ancestral sequence (see main text). The bold and dotted lines represent duplication and conversion events, respectively, and the location of each line indicates the time of the event. In this example, the simulated human lineage has a total of 18 duplication and 8 conversion events from the starting ancestral sequence.