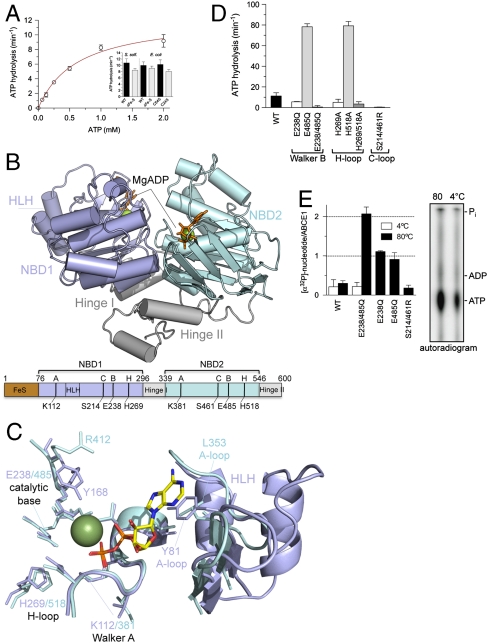
Fig. 1.
Structure and function of ABCE1. (A) ATPase activity of ABCE1 (5 μM) at 80 °C. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Data represented as mean ± SEM are fitted to the Michaelis–Menten equation. The ATP turnover rate kcat of various FeS cluster mutants (5 μM) is shown as insert. (B) X-ray structure of ABCE1ΔFeS-E238/485Q from S. solfataricus (side view). In the open ADP-bound state, ABCE1 shows a V-like architecture with NBD1 (pale blue) and NBD2 (cyan) preoriented via the hinge domain (gray). The two bound Mg-ADP molecules are shown as green spheres and orange sticks. Functional domains and critical residues in the Walker A and B motifs, C- and H-loop are illustrated below. (C) Overlay of the conserved motifs and catalytic residues of NBD1 (pale blue) and NBD2 (cyan) with regard to the bound Mg-ADP (ADP as sticks, Mg2+ as green sphere). Notably, the catalytic Glu 238 and 485 are exchanged to Gln in the X-ray structure. (D) ATP turnover rate kcat of ABCE1 mutants (5 μM) with substitutions in conserved motifs (Walker B motifs, H- and C-loop). All experiments were performed in triplicates at 80 °C. (E) Stoichiometry of occluded nucleotides. ABCE1 mutants (5 μM) were incubated with 500 μM ATP (traced with [α-32P]-ATP) at 4 °C (white) or 80 °C (black bars). Free and bound nucleotides were separated by spin-down gel filtration and quantified by Cerenkov counting. Data from two independent experiments performed in triplicates are represented as mean ± SEM. The nucleotides occluded in ABCE1E238/485Q were identified by thin layer chromatography (Right).