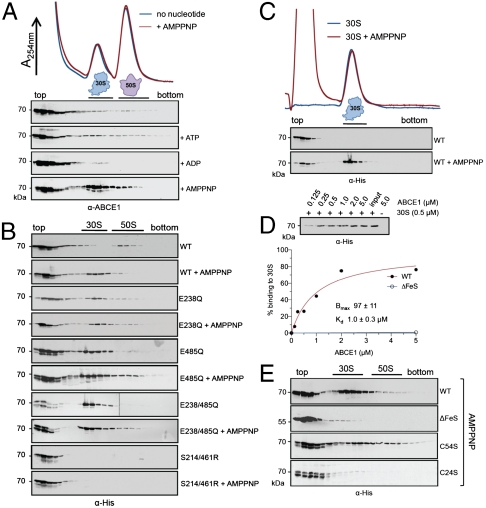
Fig. 2.
The ATP-occluded state and the FeS cluster domain of ABCE1 are essential for stable ribosome association. (A) Ribosome association of ABCE1 was analyzed by SDG in 100 μL of WCE (15 mg/mL) from S. solfataricus incubated in the presence of different nucleotides at 73 °C for 4 min. Fractions (0.5 mL) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-ABCE1 antibody. (B) Isolated ABCE1 mutants (0.4 μM) were incubated with 100 μL of S. solfataricus WCE (15 mg/mL) with and without 5 mM of AMPPNP and analyzed as described above using an anti-His antibody. (C) Binding of ABCE1WT (1 μM) to isolated 30S particles (1 μM) assayed by SDG analysis in the presence and absence of AMPPNP (5 mM) at 73 °C for 4 min. (D) Ribosome pelleting assays of ABCE1WT and isolated 30S subunits (0.5 μM) reveal a stoichiometric (1∶1) binding in the presence of AMPPNP. The amount of ABCE1WT expected for 100% binding (0.5 μM) is given as input. Data were analyzed by quantitative immunoblotting and fitted according to a one-site binding isotherm. (E) SDG analysis of FeS cluster mutants. Purified ABCE1WT, ABCE1ΔFeS, ABCE1C54S, or ABCE1C24S (0.2 μM of each) was added to 100 μL S. solfataricus WCE (15 mg/mL) and incubated with 5 mM of AMPPNP at 73 °C for 4 min. Fractions were probed with an anti-His antibody.