Figure 7.
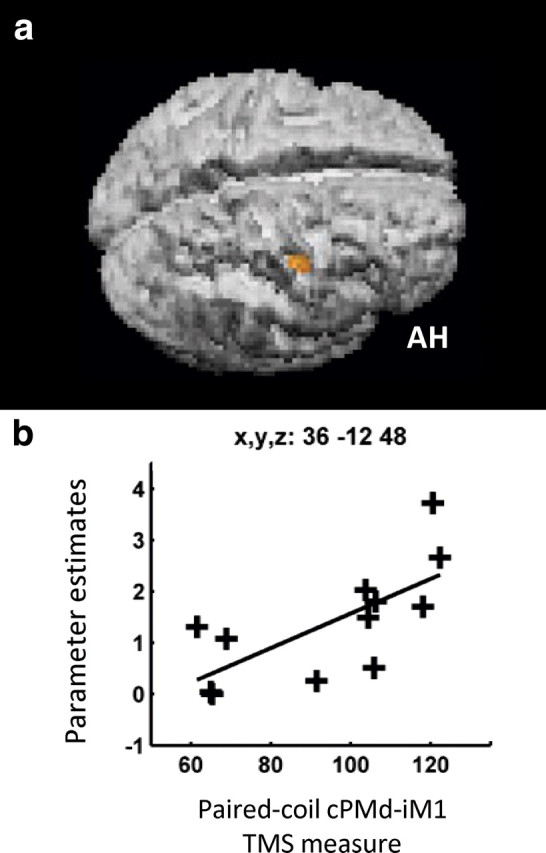
Brain regions in which the influence of cPMd during hand grip (as measured with concurrent TMS-fMRI) was greater when cPMd had a less inhibitory/more facilitatory affect on ipsilesional M1 (as measured with paired-coil TMS). a, The SPM for the correlation seen in ipsilesional posterior central sulcus, BA4p, is overlaid on the rendered mean structural scan from all patients. b, Each patient's parameter estimate for the interaction term TMShigh (grip–rest) > TMSlow (grip–rest) in ipsilesional posterior central sulcus, BA4p, plotted against the paired-coil measure of the interhemispheric cPMd-iM1 influence. AH, Affected hemisphere.
