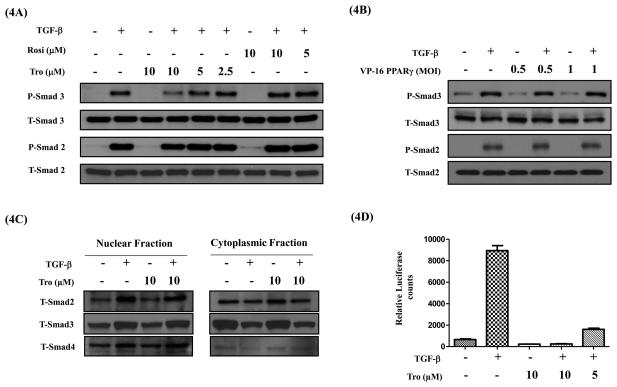
Figure 4. PPAR- γ ligands do not inhibit TGF-β induced Smad phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, but inhibit Smad functional activity.
A549 cells were serum starved for 24 h, stimulated with TGF-β (5 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of PPAR- γ ligands rosi or tro (A) or VP16-PPAR- γ (B) for 1 h. Cell lysates were assessed for phospho-Smad 2 and 3 and total Smad 2 and 3 protein levels by Western immunoblotting. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were prepared and assessed for total Smad 2, 3 and 4 protein levels by Western immunoblotting (C). For functional activity measurements A549-SBE-Luc cells were serum starved for 24 h, stimulated with TGF-β (5ng/ml) in the presence or absence of tro at indicated concentrations. At the end, luciferase expression was measured and normalized to the protein concentrations (D). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments.