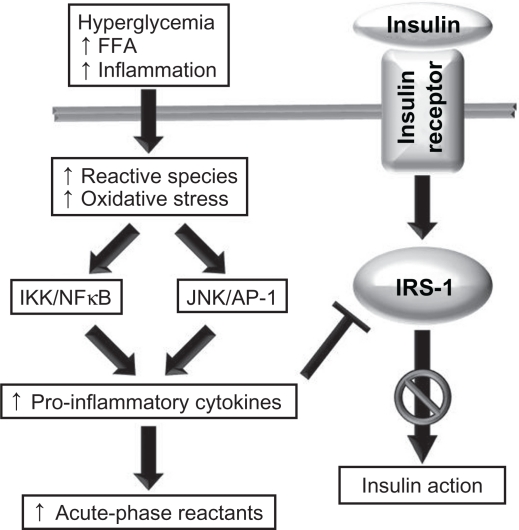
Figure 2.
The role of oxidative stress and inflammation in insulin resistance. A number of stimuli, such as hyperglycemia, high levels of circulating free fatty acid (FFA), and chronic inflammation, lead to increases in the production of reactive molecular species, and this in turn may lead to oxidative stress. Oxidants activate the JNK/AP-1 and IKK–NFκB axes, leading to an upregulation in the transcription of proinflammatory cytokine genes and increased production of cytokines and acute-phase reactants. Cytokines impair the action of the insulin receptor substrate, resulting in impaired insulin action.