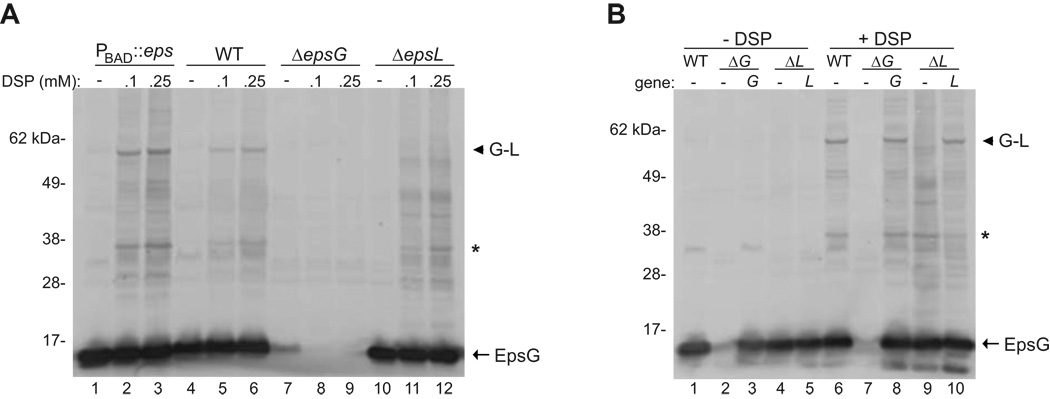
Figure 1. In vivo cross-linking of EpsG and EpsL.
(A) Whole cells of V. cholerae TRH7000 wild-type, ΔepsG, ΔepsL, and PBAD::eps (native eps promoter replaced by arabinose inducible promoter and grown in the presence of 0.01% arabinose) were cross-linked using the indicated concentrations of DSP as described in the experimental procedures, and immunoblotted for EpsG. (B) Whole cells of PBAD::eps wild-type containing pMMB67 vector, PBAD::ΔepsG with empty vector or vector encoded epsG, and PBAD::ΔepsL with empty vector or vector encoded epsL were cross-linked with 0.1 mM DSP and immunoblotted for EpsG. The position of EpsG is indicated. An arrow head designates the EpsG-EpsL complex, and an asterisk represents the putative EpsG dimer. The band directly below the putative EpsG dimer is presumed to be cross-reactive as it is also observed in the absence of DSP. The molecular weight markers are shown in kilo Daltons and lane numbers are indicated.