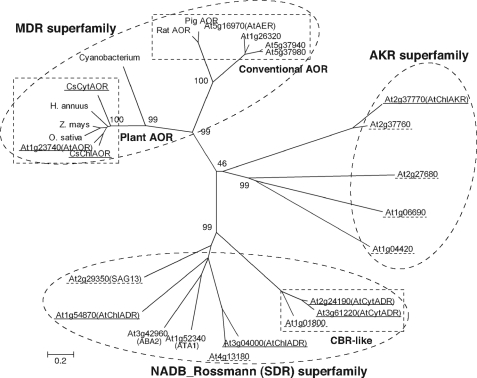
FIGURE 8.
Phylogenetic analysis of amino acid sequences of enzymes involved in NADPH-dependent reduction of reactive carbonyls. Unrooted trees were constructed using MEGA version 4 software based on the ClustalW multiple alignment according to the neighbor-joining method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. Dashed circles and rectangles show superfamilies and subfamilies, respectively. Enzymes analyzed in this study are underlined by solid lines. Expressed proteins not showing carbonyl-reducing activity are underlined by dashed lines. Other sequences are representative example of ally alcohol dehydrogenase (At1g26320, At5g37940, and At5g37980) and plausible phytohormone-metabolizing SDRs (At1g52340 (ATA1) and At3g42960 (ABA2)). Accession numbers of plant AORs are BAJ23910 (CsChlAOR), BAJ23911 (CsCytAOR), AAK66565 (Helianthus annuus, sunflower), BAF23605 (Oryza sativa, rice), ACG41966 (Zea mays, maize), and AAM16188 (AtAOR). Homologous sequence of cyanobacterium is referred from accession number YP_722551. Accession numbers of rat and pig AORs are AAH89775 and BAA08381, respectively. MDR, medium-chain dehydrogenase/reductase.