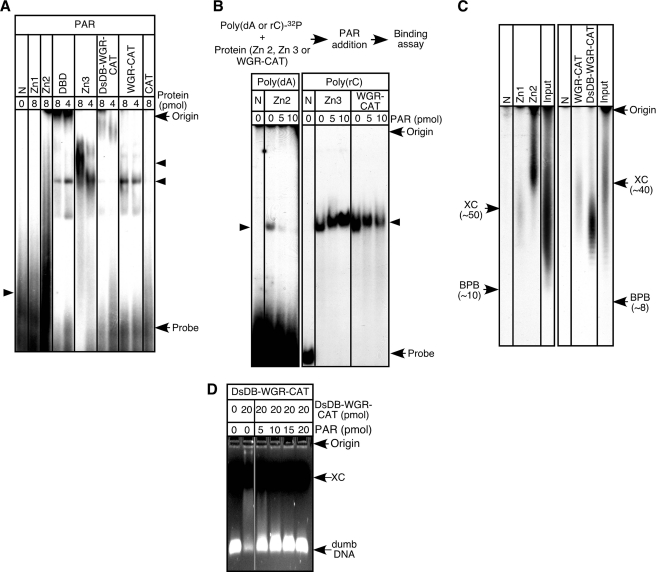
FIGURE 6.
Binding of ADP-ribose polymer to PARP-1 functional domains. A, binding assays were carried out with 32P-labeled ADP-ribose polymers (30 pmol) and PARP-1 domains. N, no protein; PAR, ADP-ribose polymers. B, Zn2 (12 pmol) was preincubated with 32P-labeled poly(dA) (30 pmol) for 15 min at room temperature. Alternatively, Zn3 and the WGR-CAT fragment (12 pmol) were incubated with 32P-labeled poly(rC) (30 pmol). Then, ADP-ribose polymers were added. The resulting samples were analyzed by 7.5%-native acrylamide gel electrophoresis. C, binding assays were carried out with 32P-labeled ADP-ribose polymers (30 pmol) with either FLAG-tagged Zn1 or FLAG-tagged Zn2 (20 pmol). Then, these fingers were pulled down by anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel. After washing of the precipitates, zinc fingers were denatured, and 32P-labeled ADP-ribose polymers were analyzed using urea-10% polyacrylamide gels. When FLAG-tagged WGR-CAT or DsDB-WGR-CAT fragment was used, 20 pmol of poly(dC) was included in the reaction mixture, and fractionation of 32P-labeled ADP-ribose polymers was carried out by using urea-15% polyacrylamide gels. For urea-10% polyacrylamide gels, xylene cyanol (XC) and bromphenol blue (BPB) migrated around 50 and 10 in length of ADP-ribose residues. For urea-15% polyacrylamide gels, xylene cyanol and bromphenol blue migrated around 40 and 8 in length of ADP-ribose residues. D, the DsDB-WGR-CAT fragment was incubated with dumbDNA (10 pmol) for 15 min at 37 °C, and then ADP-ribose polymers were added. After a 15-min incubation at 37 °C, DNA mobility assays were carried out on ethidium bromide-1.5% agarose gels.