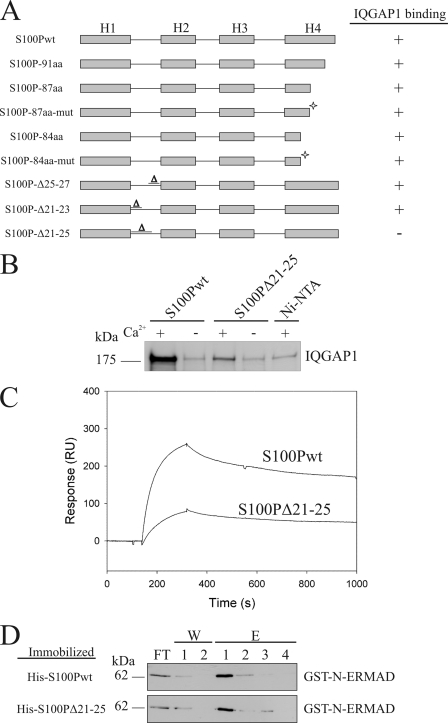
FIGURE 5.
Mapping of the IQGAP1-binding site in S100P. A, overview of the different S100P mutants that were tested for IQGAP1 binding. Binding or no binding is indicated by + or −. C-terminally truncated mutants, some containing additional mutations in helix 4 as indicated by an asterisk (S100P-87aa-mut: T82A, S83L, H86N; S100P-84aa-mut: T82A, S83L), as well as mutants with deletions in the first EF hand loop were analyzed in comparison with the full-length protein. B, amino acids (aa) 21–25 are essential for IQGAP1 binding. [35S]Methionine-labeled full-length IQGAP1 was added to immobilized His-S100Pwt or His-S100PΔ21–25 in the presence or absence of Ca2+. Bound IQGAP1 was detected by autoradiography. Note the strongly reduced amount of IQGAP1 bound to immobilized S100PΔ21–25 as compared with S100Pwt. C, SPR analysis comparing the binding of IQ to S100Pwt and S100PΔ21–25. 3000 response units (RU) of S100Pwt or S100PΔ21–25 were immobilized on a CM5 sensorchip. Sensorgrams were recorded following the injection of purified IQ domain on the immobilized S100P proteins in the presence of 50 μm Ca2+. D, analysis of the interaction of S100PΔ21–25 and S100Pwt with ezrin's N-ERMAD. GST-N-ERMAD was added to the immobilized His-tagged S100P proteins in the presence of Ca2+, and flow-through fractions were collected (FT). After washing with a Ca2+-containing buffer (W), bound GST-N-ERMAD was eluted with EGTA (E). The collected fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting using a monoclonal anti-GST antibody.