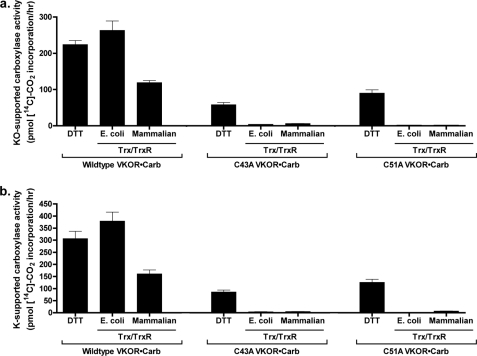
FIGURE 10.
Mutations in VKOR residues Cys43 and Cys51 disrupt Trx/TrxR-mediated, VKOR-supported carboxylation. Microsomes from insect cells coinfected with baculoviruses containing the carboxylase and wild type or mutant VKORs were washed with sodium carbonate and then assayed in a carboxylation reaction in the presence of vitamin K epoxide (KO) (a) or vitamin K quinone (K) (b) and the indicated reductants as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The activities observed are presented to indicate the absolute level of signal. The values observed for DTT-supported C43A and C51A activities corresponded to 8000 or 12,000 cpm in the assay, respectively, and these values are 20–30-fold over background. The entire experiment was performed twice, giving similar results.