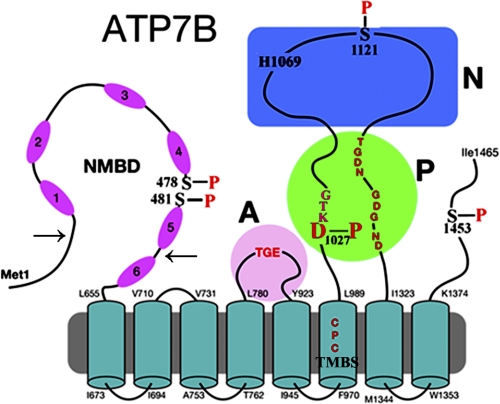
FIGURE 1.
Two-dimensional folding model of ATP7B sequence. The diagram shows eight transmembrane segments, including a copper binding site (TMBS). The extramembranous region comprises a nucleotide binding domain (N) with the His-1069 residue whose mutation is frequently found in Wilson disease; the P domain with several residues (in red) conserved in P-type ATPases where Asp-1027 undergoes phosphorylation to form the catalytic phosphoenzyme intermediate (EP), the A domain with the TGE conserved sequence involved in catalytic assistance of EP hydrolytic cleavage, the NMBD with six copper binding sites, and a C-terminal chain. Note that serines shown to be phosphorylated (5) reside within flexible loops of the protein (see “Discussion”). These are Ser-478 and Ser-481 (NMBD), Ser-1121 (N domain), and Ser-1453 (C-terminal tail). The arrows on the NMBD delimit the segment that was deleted to obtain the Δ5 construct.