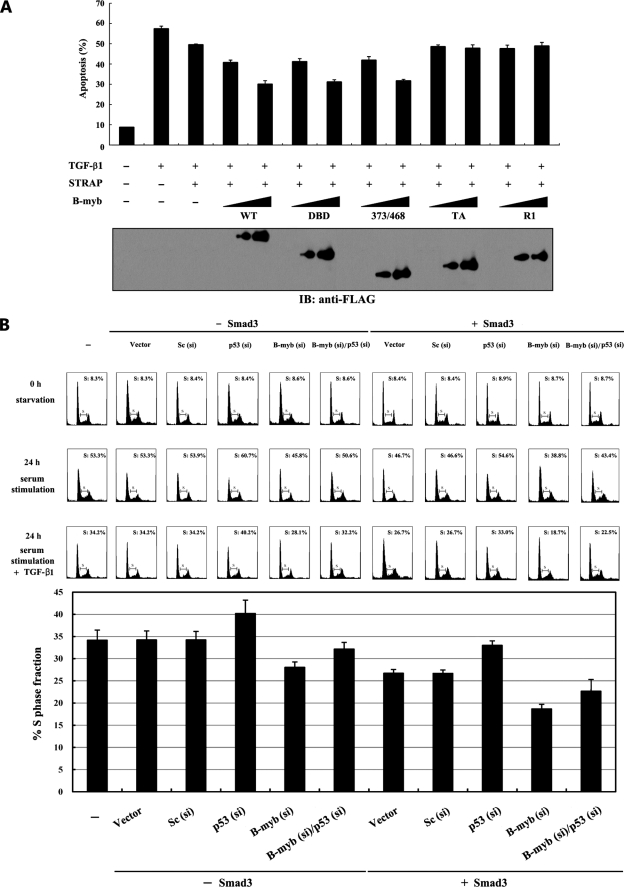
FIGURE 7.
Suppression of TGF-β-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition by B-MYB. A, B-MYB inhibits TGF-β-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. HaCaT cells were transiently transfected with increasing amounts (1.5 and 3 μg) of wild-type B-MYB or its deletion mutants (DBD, 373/468, TA, and R1) as indicated, together with an expression vector encoding GFP (2 μg). Transfected cells were treated with TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) for 20 h to induce apoptosis. Apoptotic cell death was determined using the GFP expression system as described previously (4). The expression level of FLAG-tagged wild-type B-MYB and its deletion mutants was analyzed by anti-FLAG antibody immunoblot. B, effect of B-MYB on TGF-β-induced cell cycle arrest. HepG2 cells (∼2 × 105/dish) transfected with the indicated siRNA duplexes (200 nm B-MYB siRNA #1, B-myb (si), 100 nm p53 siRNA, p53 (si), or 200 nm control scrambled siRNA, Sc (si)) in the presence or absence of SMAD3 (3 μg) were synchronized in G0/G1 by hydroxyurea (2 mm) treatment for 20 h. Cells were collected before (0 h starvation) or after 10% serum treatment for 24 h in the absence (24 h serum stimulation) or presence (24 h serum stimulation + TGF-β1) of TGF-β1 (100 pm), and the percentage of cells in the G1, S, or G2/M phases was analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graphs (lower panel) represent the fraction of cells in S phase (24 h serum stimulation + TGF-β1). si, siRNA.