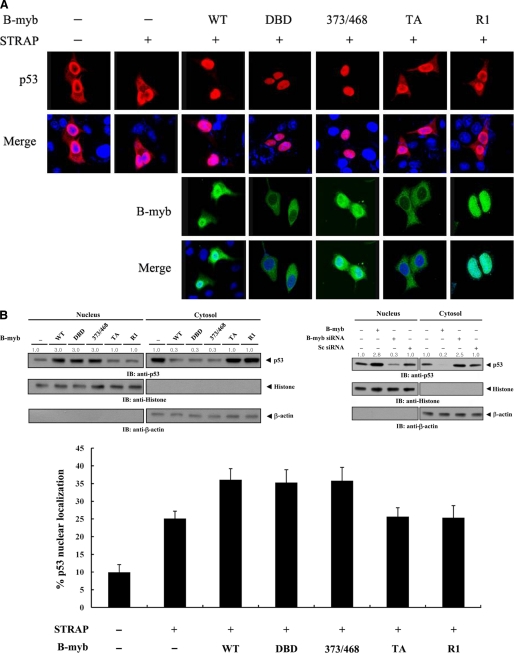
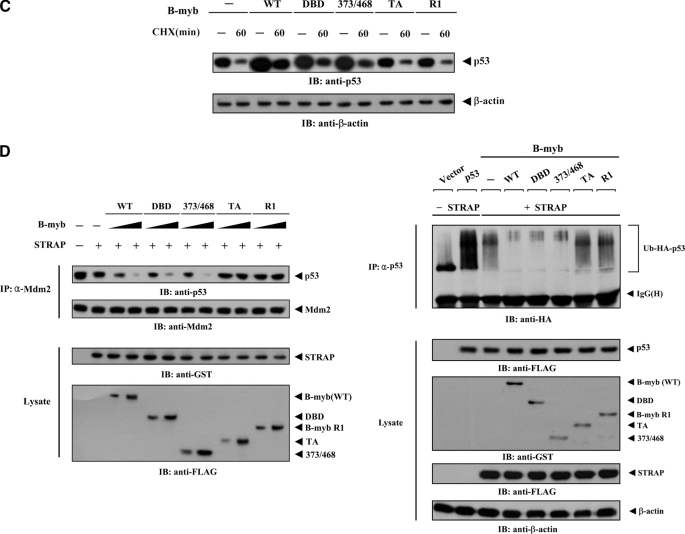
FIGURE 9.
Modulation of p53 localization by B-MYB. A, MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated expression vectors for wild-type (WT) and deletion mutants (DBD, 373/468, TA, and R1) of B-MYB, together with or without STRAP, in the presence of p53. Cells were immunostained with anti-p53 antibody, followed by Alexa Fluor-594 anti-rabbit secondary antibody (red, for p53), and analyzed by confocal microscopy. B-MYB subcellular localization was determined by immunostaining with anti-FLAG and Alexa Fluor-488 anti-mouse secondary antibodies (green, for B-MYB). Nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI. B, confirmation of endogenous p53 localization by immunoblot analysis. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of MCF7 cells transfected with the indicated expression vectors or a B-MYB-specific siRNA #1 were analyzed by immunoblot using the indicated antibodies (upper panels). Nucleus and Cytosol indicate the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. The relative level of p53 expression was quantified by densitometric analysis. The fold-increase relative to untransfected samples in parental MCF7 cells was calculated. The percentage of p53 nuclear localization was calculated as the number of p53-positive cells with a nuclear localization divided by the total number of p53-positive cells (lower panel). About 300 cells were analyzed per sample using a confocal microscopy. C, measurement of p53 stability by immunoblot analysis. MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated expression vectors. Time intervals indicate the number of minutes after 20 μg/ml of cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. D, effect of B-MYB on p53·MDM2 complex formation and p53 ubiquitination. HCT116 cells were transfected with increasing amounts (0.8 and 1.6 μg) of wild-type or deletion mutants of B-MYB in the presence or absence of STRAP. The cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with an anti-MDM2 antibody (IP: α-Mdm2), and immunoblotted (IB) with an anti-p53 antibody to determine the endogenous levels of p53·MDM2 complex formation (left, top panel). To measure B-MYB-mediated modulation of p53 ubiquitination, p53-null HCT116 cells were transfected with vectors expressing HA-tagged ubiquitin (Ub), p53, and wild-type or deletion mutants of B-MYB as indicated (2 μg each), in the presence or absence of STRAP. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-p53 antibody (IP: α-p53) and immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody to determine the level of p53 ubiquitination (right, top panel).