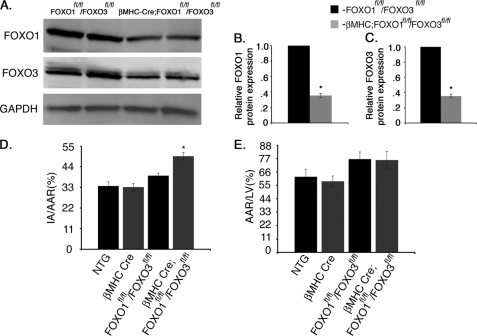
FIGURE 3.
βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl mice have increased ischemic injury. A, Western blot assessment of total protein expression of both FoxO1 and FoxO3 in control (FoxO1fl/flFoxO3fl/fl) and cardiomyocyte-specific FoxO1- and FoxO3-deficient (βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl) mouse hearts. B and C, quantitative representation of A showing 70% reduction of both FoxO1 and FoxO3 in βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl mouse hearts compared with FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl controls. D and E, NTG, βMHC-Cre, FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl, and βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl mouse hearts were subjected to 1 h of ischemia followed by 24 h of reperfusion and were stained with triphenyltetrazolium chloride and Evan's blue dye to determine cell viability and the area at risk. Quantification of infarct area (IA) versus AAR shows significant increase in percentage of I/R injury with no significant changes in AAR in βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl compared with NTG, βMHC-Cre, and FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl mouse hearts. Significance was determined by Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; for NTG, n = 6, βMHC-Cre, n = 7, FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl, n = 7, and for βMHC-Cre;FoxO1fl/fl/FoxO3fl/fl, n = 8).