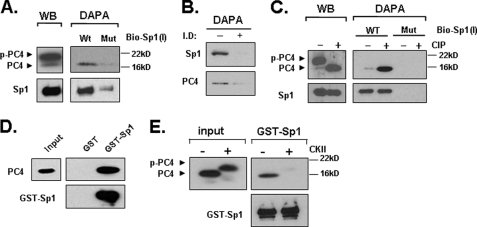
FIGURE 3.
PC4 associates with Sp1 at the LHR promoter and phosphorylation of PC4 prevents this association. A, nuclear proteins isolated from MCF-7 cells were analyzed by Western blot (left) for expression of PC4 and Sp1, or by DAPA using 5′-biotin-labeled wild type Sp1–1 probe (WT) or its mutant oligomer devoid of Sp1 binding activity (Mut) (right). The avidin-precipitated protein complexes were analyzed by Western blots with PC4 and Sp1 antibodies. p-PC4 represents the phosphorylated form of PC4. B, Sp1-immunopleted nuclear proteins from MCF-7 cells and control samples were analyzed by DAPA using 5′-biotin-labeled wild type Sp1–1 probe followed by Western blot with Sp1 and PC4 antibodies. I.D, immunodepleted; −, control; +, nuclear extracts immunodepleted of Sp1 by Sp1 antibody (see “Experimental Procedures”). C, nuclear extracts from MCF-7 cells were treated with or without calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP) for 15 min at room temperature, and analyzed by Western blot (WB) for expression of PC4 and Sp1 (left), or precipitated by the WT or Mut Sp1–1 probe with DAPA (right). D, GST and GST-Sp1 was immobilized to GST·BindTM-agarose beads and incubated with 100 units of recombinant PC4 protein. The pull-down samples were analyzed with immunoblotting with anti-PC4 antibody. The blot was also probed with anti-Sp1 antibody. E, GST-pull down assay of non-phosphorylated and CKII-phosphorylated PC4 with GST-Sp1. The pull-down samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PC4 and anti-Sp1 antibody. Input represents 5% of the total PC4 protein used in each assay.