Figure 1.
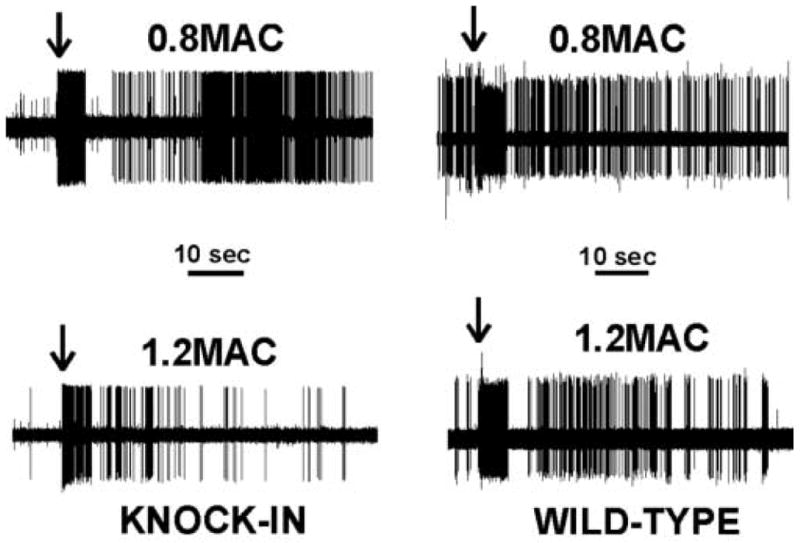
Shown are action potential recordings from knock-in and wild-type mice at 0.8 and 1.2 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of isoflurane. Arrows indicate the time at which the pinch was applied to the receptive field on the hindpaw. Isoflurane depressed the responses from 0.8 to 1.2 MAC in both wild-type and knock-in animals.
