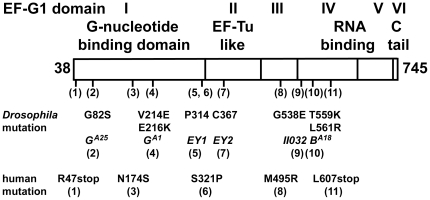
Figure 3. The identified mutations in EF-G1 are located in various domains.
Similarities between EF-G1 and bacterial G-factors indicate that the proteins likely share a similar three-dimensional structure [20]. The first and largest domain of EF-G1 is its GTP-GDP binding domain. Six of the identified mutations are located in this domain. The second domain shares homology to the elongation factor EF-Tu. Domains IV and V show similarities with other RNA binding proteins, and structural analysis suggests that Domains III, IV, and V form an interface mimicking the shape of a tRNA that is used to interact with ribosomes [13]. In addition to bacterial G-factors and mitochondrial EF-G2 proteins, EF-G1 contains a positively charged C-terminal tail. The deletion EY1 removes 1888 nucleotides, which creates a stop codon six amino acids after P314 and encodes a truncated protein that only consists of the first domain. Similarly, deletion EY2 removes 3663 nucleotides, which creates a stop codon 19 residues past C367 and encodes a protein truncated within domain II.