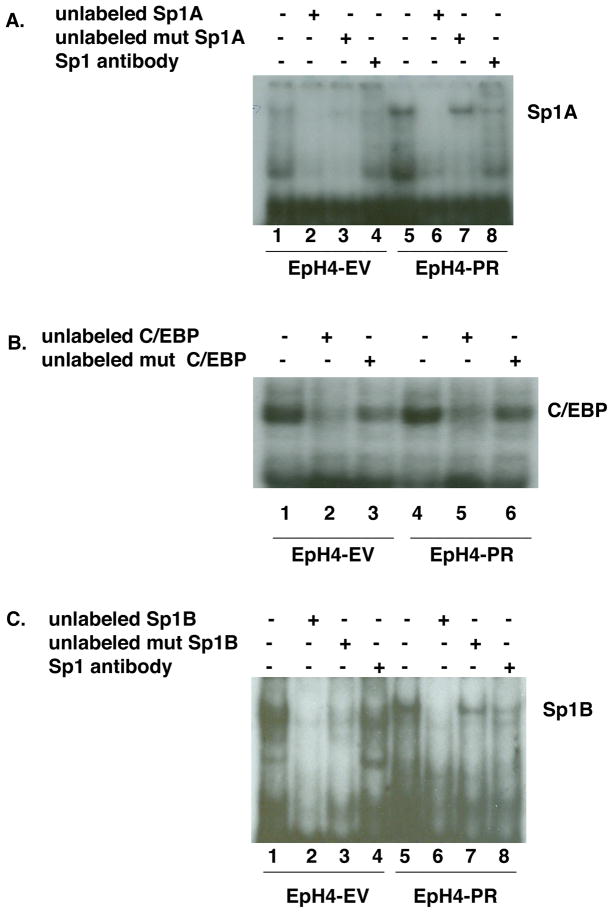
Fig. 5.
Analysis of DNA binding proteins present in EpH4-EV and EpH4-PR cells.
A. Nuclear extracts were prepared from EpH4-EV (lanes 1–4) and PR (lanes 5-8) cells that were first grown in media containing 10% FBS and then switched to media containing 5% CSS for 24 hr. Extracts were incubated in all cases with 32P-Sp1A oligonucleotide probe either alone (lanes 1 and 5) or with an excess of unlabeled Sp1A oligo (lanes 2 and 6), an excess of unlabeled mutant Sp1A oligo (lanes 3 and 7) or with Sp1 antibody (lanes 4 and 8) to determine specificity.
B. The nuclear extracts from (A) were incubated in all cases with 32P-C/EBP oligonucleotide probe either alone (lanes 1 and 4) or with an excess of unlabeled C/EBP oligo (lanes 2 and 5) or an excess of unlabeled mutant C/EBP oligo (lanes 3 and 6) to determine specificity.
C. The nuclear extracts from (A) were incubated in all cases with 32P-Sp1B oligonucleotide probe either alone (lanes 1 and 5) or with an excess of unlabeled Sp1B oligo (lanes 2 and 6), an excess of unlabeled mutant Sp1B oligo (lanes 3 and 7) or with Sp1 antibody (lanes 4 and 8) to determine specificity.