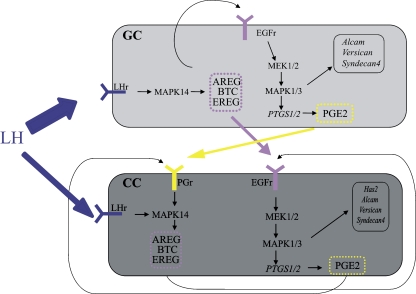
Fig. 1.
The interactions occuring in the ovarian mural granulosa cells (GC) and cumulus cells (CC) after the administration of hCG for ovulation induction. The hypothetical figure is based on earlier literature [16, 56, 57]. LH will mainly act on the mural granulosa cells where it will induce the production of Egf like family members: Amphireguline (Areg), Betacelluline (Btc), Epireguline (Ereg). All can bind to the Egf receptor (Egfr) present in both GC and CC. Egfr stimulation involves the MEK1/2 and MAPK1/3 pathway and will induce Ptgs expression and therefore the production of Prostaglandin E2 (Pge2). Both prostaglandin and the Egf like family members are secreted by GC and can transduce the ovulatory response in the CC and also have an autocrine function in the CC. The ovulatory response will trigger the production of Hyaluronic acid synthetase 2 (Has2), Versican (Vcan) and activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (Alcam), genes occuring predominantly in the CC. The expression of Ptgs1 and Syndecan 4 (Sdc4) in GC or CC was not earlier documented so its involvement as represented here needs to be further documented