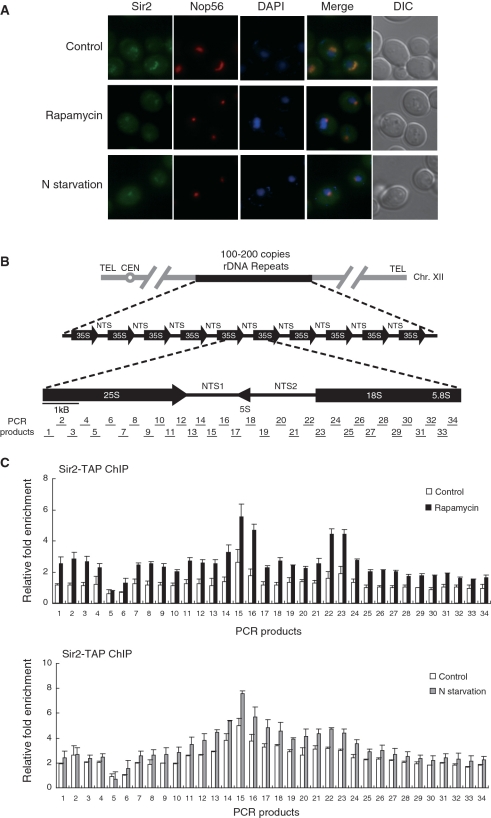
Figure 1.
TORC1 inhibition leads to condensation of the nucleolus and enhancement of association of Sir2 with rDNA. (A) Rapamycin treatment and nitrogen starvation cause reduction of the nucleolar size and condensation of the Sir2-GFP signal. Subcellular localization of Sir2-GFP (green) and Nop56-RFP (red) was analyzed after treatment with 200 ng/ml rapamycin or incubation in nitrogen-depleted medium for 1 h. DAPI staining for visualization of the nucleus (blue) and differential interference contrast (DIC) images are also shown. (B) The structure of the tandemly repeating rDNA of S. cerevisiae is shown above, and a single 9.1-kb rDNA unit is shown expanded below. PCR products analyzed in the ChIP assays are indicated below the rDNA unit. (C) Rapamycin treatment and nitrogen starvation enhance association of Sir2 with rDNA. The degree of Sir2 binding to rDNA was measured using the ChIP assay after treatment with 200 ng/ml rapamycin (upper panel) or incubation in nitrogen-depleted medium for 1 h (lower panel). For control, cells were treated with DMSO only (upper panel) or grown in SC medium (lower panel). Relative fold enrichment refers to the relative ratio of PCR products amplified from immunoprecipitated DNA to products from whole-cell extract DNA. Values represent the average of three independent experiments and error bars indicate standard deviations.