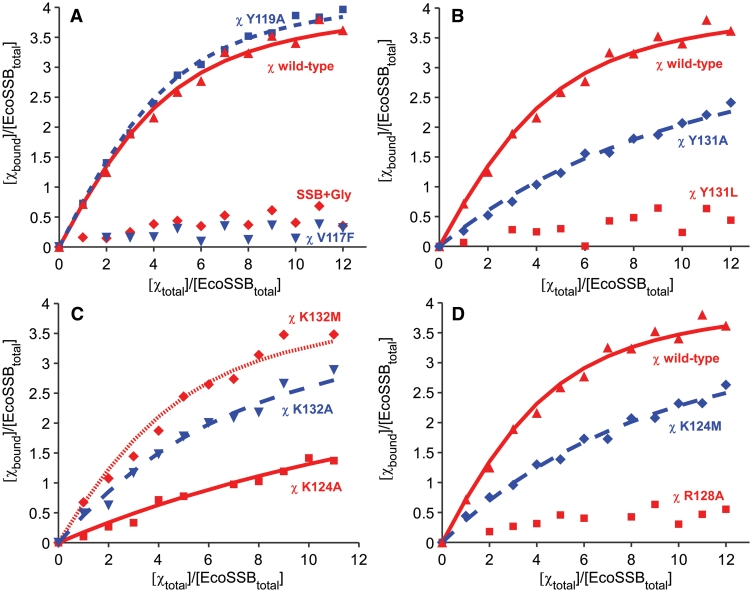
Figure 1.
Interaction of different mutants of EcoSSB and χ under high salt conditions. An amount of 2.5 µM of EcoSSB was mixed with different amounts of χ in a buffer containing 20 mM potassium phosphate pH 7.4, 0.3 M NaCl and 0.5 mM DTT and analysed in sedimentation velocity experiments in an analytical ultracentrifuge. In A, B and D, a binding isotherm fitted to the data of the interaction of EcoSSB and χ wild-type (red triangle) with KA = (2.9 ± 1) × 105 M−1 and n = 4.2 is shown for comparison (solid red line). (A) Exchanging V117 to phenylalanine (inverted blue triangle) dramatically lowered the binding affinity between χ and EcoSSB. Also an extension of SSB by a C-terminal glycine (SSB+Gly) disabled interaction with χ (red rhombus). Replacing Y119 by alanine (blue square) did not significantly change the affinity of χ to SSB [dashed blue line: KA = (3.4 ± 1) × 105 M−1 and n = 4.2]. (B) Exchanging tyrosine 131 of χ to leucine dramatically lowered the binding affinity to SSB (red square), whereas χ Y131A retained some of its activity (blue rhombus). The dashed blue line represents a binding isotherm fitted to the data of χ Y131A binding to EcoSSB with KA = (4.8 ± 1) × 104 M−1, n = 4.2. (C) The K124A mutation had a strong effect on the SSB/χ interaction (red square), lowering KA to (2.1 ± 0.5) × 104 M−1 with n = 4.2 (solid red line). The χ K132A mutant (blue triangle) also displayed a lowered binding affinity to SSB [dashed blue line: KA = (9 ± 2.5) × 104 M−1 and n = 4.2]. χ K132M (red rhombus) behaved similar to wild-type protein [fine dashed red line: KA = (2.1 ± 1) × 105 M−1 and n = 4.2]. (D) In order to test the new model of SSB/χ interaction, the K124M and R128A mutants of χ were generated. Both showed effects in accordance with the new model, with K124M (blue rhombus) lowering the binding affinity to SSB to a fifth compared to wild-type [dashed blue line, KA = (6 ± 1) × 104 M−1 and n = 4.2] and R128A (red squares) disabling the interaction with SSB.