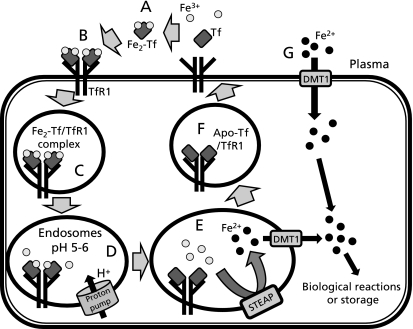
Fig. 2.
Iron metabolism in hepatocytes. A–F: TfR-dependent route (the Tf cycle). A: Two ferric irons (Fe3+) in the plasma bind to Tf with high affinity. B: Fe2-Tf binds to TfR1 on the surface of hepatocytes. C: Fe2-Tf/TfR1 complex is taken up into hepatocytes by endocytosis. D: The pH of endosomes is lowered to 5–6 by an action of proton pumps, and then Fe3+ is released at this acidic pH. E: Released Fe3+ becomes ferrous iron (Fe2+) by the enzymes of STEAP family, and then Fe2+ moves across the endsomal membrane through the DMT1 transporter. F: Apo-Tf still binds to TfR1 at the lower pH of endosomes. Apo-Tf/TfR1 is returned to the surface of the hepatocyte for further iron binding and uptake. G: TfR-independent route. At the high level of iron in plasma, NTBI is reduced to Fe2+ by ferric reductase. Fe2+ is rapidly transported into the hepatocytes through DMT1.