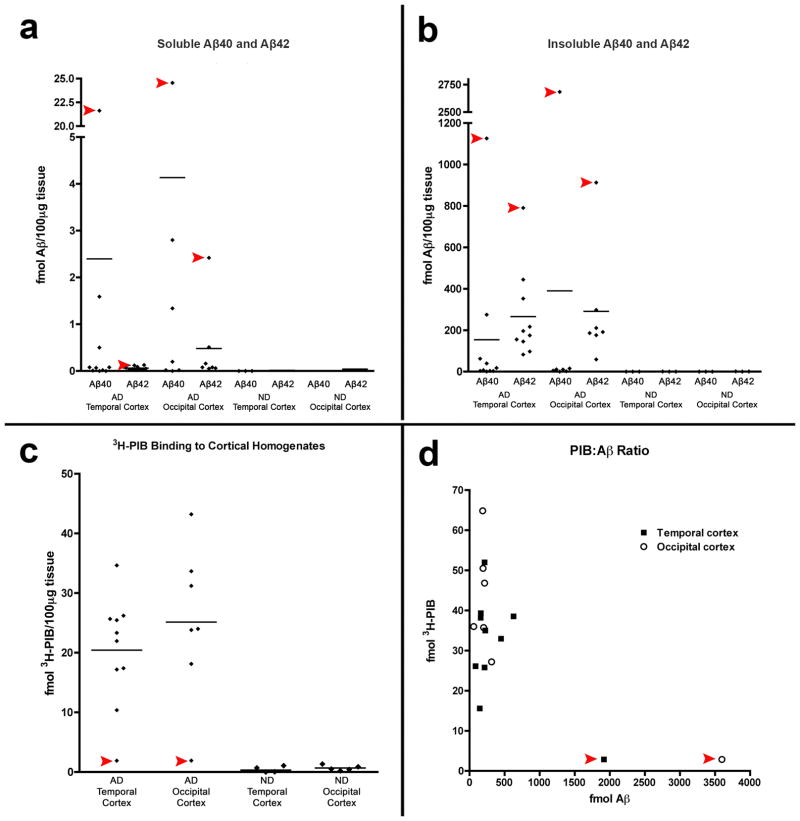
Fig. 4. Aβ levels and 3H-PIB binding in temporal and occipital cortical homogenates from AD1, nine comparison AD cases and three nondemented control (ND) cases.
(a, b) By ELISA of soluble and insoluble extracts, AD1 (red arrowheads) exhibited substantially more soluble and insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 than did all other AD cases examined in this study. Negligible Aβ was detected in both regions of the 3 ND cases (group means are indicated by the horizontal lines). Levels of soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 (a) and levels of insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 (b) are expressed in fmol Aβ per 100μg wet tissue for each subject. (c) Radioligand binding assays with 3H-PIB reveal high levels of PIB binding to temporal and occipital cortical tissue from all AD cases in this study except AD1, which showed only background levels of PIB binding. (d) The ratio of PIB binding to total Aβ in two cortical regions. When AD1 data points were excluded from the analysis, total levels of insoluble Aβ (Aβ40 and Aβ42) correlate positively with 3H-PIB binding to AD temporal (n=9) and occipital (n=7) cortical homogenates from the comparison AD cases [29].