Figure 7.
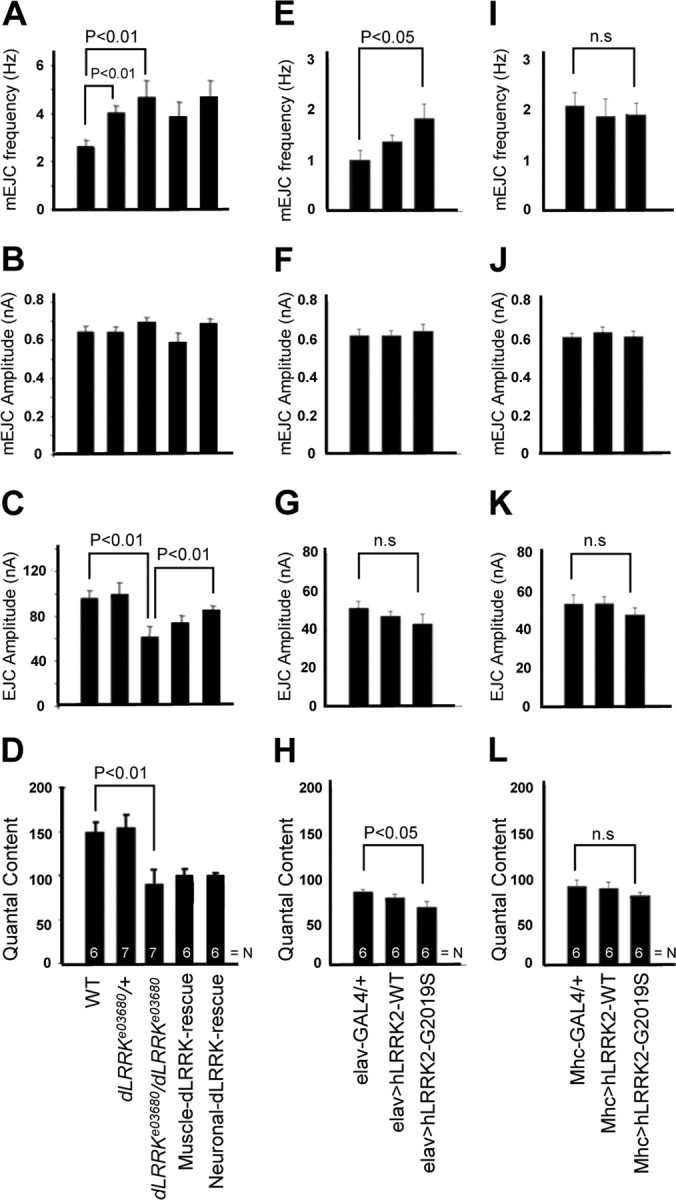
Electrophysiological phenotypes in animals with altered LRRK2 activities. Bar graphs showing quantitative analyses of mEJC frequency, mEJC amplitude, EJC amplitude, and quantal content in wild-type, dLRRKe03680/+, dLRRKe03680/dLRRKe03680, muscle dLRRK–WT-rescue, neuronal dLRRK–WT-rescue, elav–GAL4/+, elav–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–WT, elav–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–G2019S, Mhc–GAL4/+, Mhc–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–WT, and Mhc–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–G2019S animals are presented. A, E, I, mEJC frequency was increased in both dLRRKe03680/+ and dLRRKe03680/dLRRKe03680 relative to wild-type control (p < 0.01). There was no rescue of this dLRRK mutant phenotype by neuronal or muscle expression of the dLRRK transgene. mEJC frequency was increased in elav–GAL4>hLRRK2–G2019S (E) (p < 0.05) but not Mhc–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–G2019S (I) compared with elav–GAL4/+ and Mhc–GAL4/+ control, respectively. B, F, J, There was no significant change in the amplitude of mEJCs for the various genotypes compared with the corresponding controls. C, D, G, H, K, L, The EJC amplitude (C) and quantal content (D) were decreased in dLRRKe03680 mutant compared with wild-type control (p < 0.01). For EJC amplitude, there was partial rescue by neuronal but not muscle expression of the dLRRK transgene. However, for quantal content, neither neuronal nor muscle expression of the dLRRK transgene showed rescue. Although the EJC amplitude (G) was not significantly changed, quantal content (H) was decreased in elav–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–G2019S animals (p < 0.05). EJC amplitude (K) and quantal content (L) were not significantly changed in Mhc–GAL4>UAS–hLRRK2–G2019S animals. The total number of boutons quantified for each genotype is indicated by N inside the bars.
