FIGURE 2.
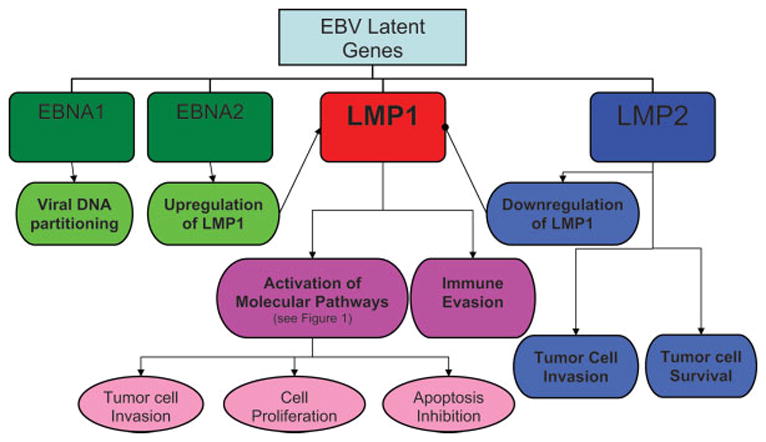
Mechanisms of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) development. NPC tumorigenesis depends on the activity of latent proteins LMP1 and 2 and EBNA 1 and 2. The majority of cancer development is propagated by LMP1, which is responsible for the activation of various molecular pathways (see Figure 1) and immune evasion. LMP1 is regulated positively by LMP2 and negatively by EBNA 2. The other functions of LMP2 include mediation of tumor cell survival and invasion. Finally, EBNA 1 is critical for viral DNA partitioning during replication.  , Stimulatory effect;
, Stimulatory effect;  , inhibitory effect; LMP, latent membrane protein; EBNA, EBV-determined nuclear antigen. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
, inhibitory effect; LMP, latent membrane protein; EBNA, EBV-determined nuclear antigen. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
