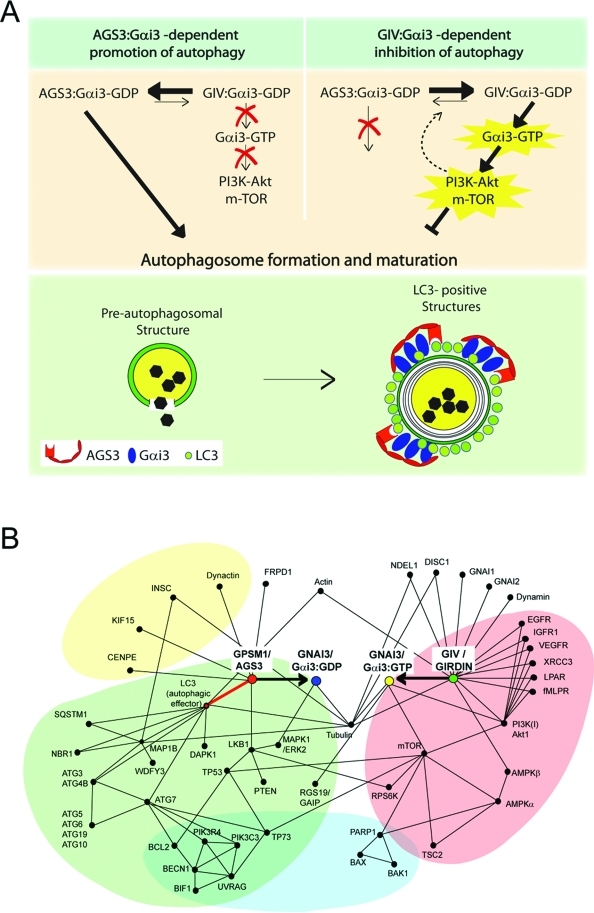
FIGURE 7:
Proposed working model and protein–protein interaction map. (A) Working model. In the absence of growth factors (top left), Gαi3 preferentially interacts with AGS3, its GDI, which maintains it inactive (Gαi3–GDP). The Gαi3–AGS3 complex localizes to LC3-positive structures via a direct interaction between AGS3 and LC3, thereby promoting autophagy (i.e., maturation of preautophagosomal structures into mature LC3-positive structures; green panel, bottom). In the presence of growth factors (top panel, right), Gαi3 is activated (Gαi3–GTP) by GIV, its GEF, which 1) enhances the anti-autophagic class I PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway at the PM and 2) releases active Gαi3 from Gαi3–AGS3–LC3 complexes assembled on membranes, thereby directly inhibiting autophagosome formation and maturation. It is possible that signaling programs modulated by GIV’s GEF function at the PM also influence the equilibrium between Gαi3–AGS3 and Gαi3–GIV as a regulatory feedback loop (interrupted arrow). Further studies will be required to pinpoint the specific LC3-positive compartment where Gαi3 localizes and the precise role of this G protein in regulating autophagosome maturation. (B) Proposed protein–protein interaction map for Gαi3, GIV, and AGS3 showing the shortest functional links that integrate pro- or anti-autophagic signaling by growth factors and G protein pathways in balancing the process (initiation and reversal) of autophagy. Functional interactions between Gαi3 and its modulators analyzed in this (GIV and AGS3) and other studies (RGS19/GAIP; Ogier-Denis et al., 1997) in the context of autophagy are shown. These are based on interactions listed in the I2D (Brown and Jurisica, 2005; Brown et al., 2009), STRING (http://string-db.org/), and MitoCheck (www.mitocheck.org) databases and validated in the literature. For simplicity, this interaction map includes only the experimentally validated functional interactions that are relevant to G protein and growth factor signaling during autophagy. The proteins of the autophagic pathway (green) are linked to Gαi3 by a direct interaction (identified in this work and highlighted with a bold red line) between the GDI AGS3 (GPSM1) and LC3 (ATG8). The proteins of the anti-autophagic growth factor/nutrients (growth factor receptors, G protein–coupled receptors) and mTOR signaling pathways (red) are linked to G protein signaling via GIV (Girdin), the GEF that directly interacts with and activates Gαi3 (resulting in Gαi3–GTP). The protein network also reveals that processes such as apoptosis (blue) and asymmetric cell division (yellow) are likely to be influenced by modulation of G protein activity by either this or other such pairs of GDI(s) and GEF(s).