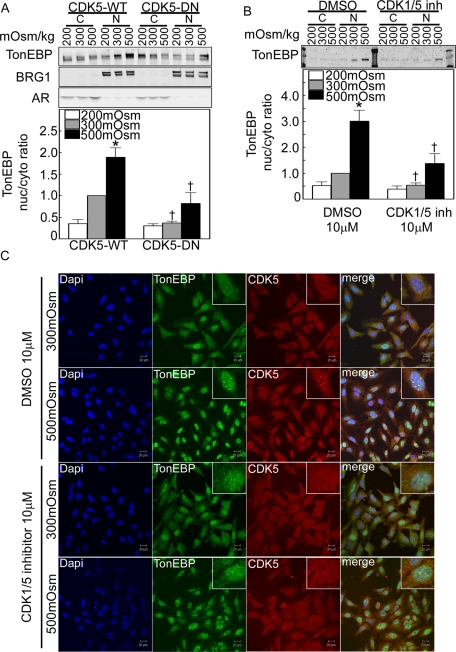
FIGURE 5:
CDK5 contributes to regulation of TonEBP/OREBP nuclear localization. (A) and (B) Inhibition of CDK5 kinase activity abolishes high NaCl–induced nuclear localization of TonEBP/OREBP. Western analysis was performed on proteins extracted from cytoplasm and nucleus, using antibodies against TonEBP/OREBP. (A) HEK293 cells transiently transfected with CDK5 wild-type (CDK5-WT) or dominant-negative kinase dead (CDK5-DN) were incubated for 2 h at 200, 300, or 500 mOsm/kg (NaCl varied). Top, representative Western blot. Bottom, summary data. Cytoplasmic (aldose reductase) and nuclear (Brg1) markers rule out important cross-contamination between the respective extracts. (B) HEK293 cells were incubated for 2 h at 200, 300, or 500 mOsm/kg (NaCl varied), with or without 10 μM CDK1/5 inhibitor (CDK1/5 inh). Top, representative Western blot. Bottom, summary data (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs. 300 mOsm/kg control, †P < 0.05 control vs. experimental. (C) HeLa cells were preincubated for 1 h at 300 mOsm/kg with DMSO or with 10 μM CDK1/5 inhibitor, and then osmolality was increased to 500 mOsm/kg (NaCl added) for 1 h or kept at 300 mOsm/kg in the continued presence of CDK1/5 inhibitor or vehicle. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-TonEBP/OREBP and anti-CDK5 antibodies. Under control (DMSO) conditions at 300 mOsm/kg, TonEBP/OREBP is present in the cytoplasm, where it colocalizes with CDK5. Under control conditions at 500 mOsm/kg, TonEBP/OREBP moves into the nucleus, where it colocalizes in speckles with CDK5. The CDK1/5 inhibitor decreases both nuclear localization of TonEBP/OREBP at 500 mOsm/kg and its colocalization with CDK5 in the nucleus.