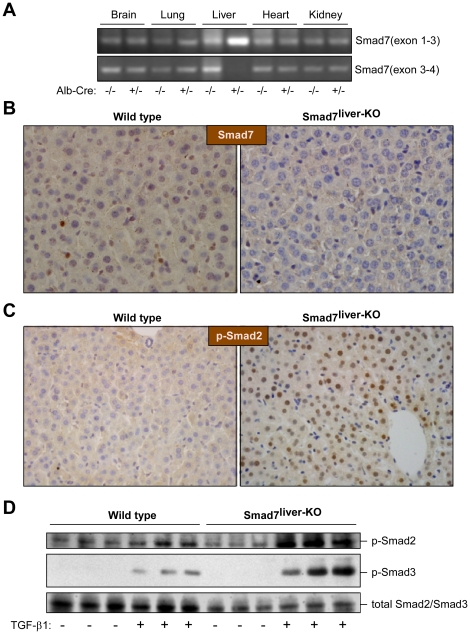
Figure 1. Characterization of Smad7liver-KO mice.
(A) Liver-specific deletion of Smad7. RT-PCR analysis was performed with total RNA isolated from multiple tissues in Alb-Cre heterozygous or wild type mice (all mice having Smad7loxP/loxP) with specific primers that amplify mRNA regions corresponding to exons 1–3 or exons 3–4 of Smad7 respectively. (B) Analysis of the Smad7 by immunohistochemistry staining. Representative liver sections (400 X) from wild type and Smad7liver-KO mice were used in immunohistochemistry staining with an anti-Smad7 antibody. The nuclei were stained with haematoxylin. (C) Smad2 phosphorylation is elevated in the liver of Smad7liver-KO mice. Smad2 phosphorylation was analyzed by immunohistochemistry using liver sections from either wild type or Smad7liver-KO mice. The nuclei were stained with hematoxylin. Note that nuclear phospho-Smad2 staining is increased in the liver of Smad7liver-KO mice. (D) TGF-β-induced Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylation is enhanced by Smad7 deletion in primary hepatocytes. Immunoblotting was performed using total protein lysate extracted from primary hepatocytes using antibodies as indicated. The cells were treated with or without 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1 for 24 hours as indicated after overnight serum starvation.