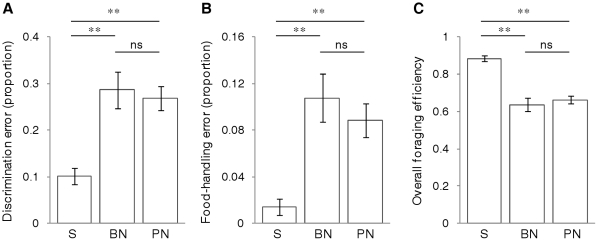
Figure 5. Acoustic noise increases foraging performance errors and reduces foraging efficiency.
Response of foraging sticklebacks to playbacks of silence (S), brief (10 s) white noise (BN) and prolonged (300 s) white noise (PN). Bars show mean±1s.e.m. response for 24 fish during each playback of a repeated-measures experiment, with significant (**p≤0.01) and non-significant (ns p≥0.05) posthoc differences indicated (paired t-tests with Bonferroni correction). Brief noise and prolonged noise both significantly affected (A) the proportion of attacks towards non-food items, (B) the proportion of attacked food items that were not consumed, and (C) overall foraging efficiency (consumed items as proportion of all attacks on food and non-food items).