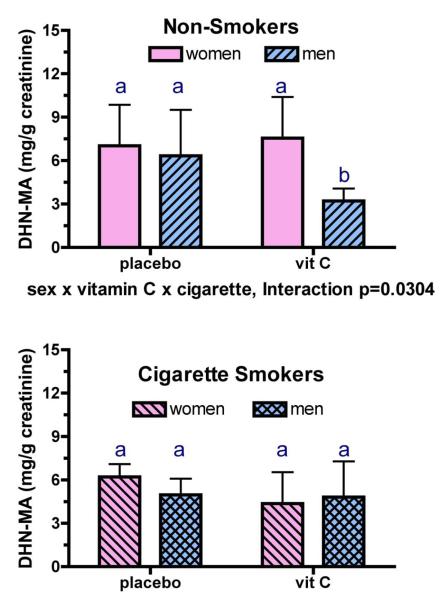
Fig. 5. Modulation of urinary DHN-MA metabolite levels (mean ± SD) by vitamin C supplements in nonsmoking men and women (top panel) and in smoking men and women (bottom panel).
Vitamin C supplementation had a different effect on urinary DHN-MA depending upon the sex and cigarette smoking habits of the participants (3-way interaction p=0.0304). As with the other metabolites, there was an overall effect of vitamin C supplementation on urinary DHN-MA (p=0.0165). Additionally, vitamin C supplementation decreased urinary DHN-MA (p<0.05) in non-smoking men compared with nonsmoking women, and also in non-smoking men compared with smoking men. Bars within a graph bearing the same letter are not different from each other.