FIG. 4.
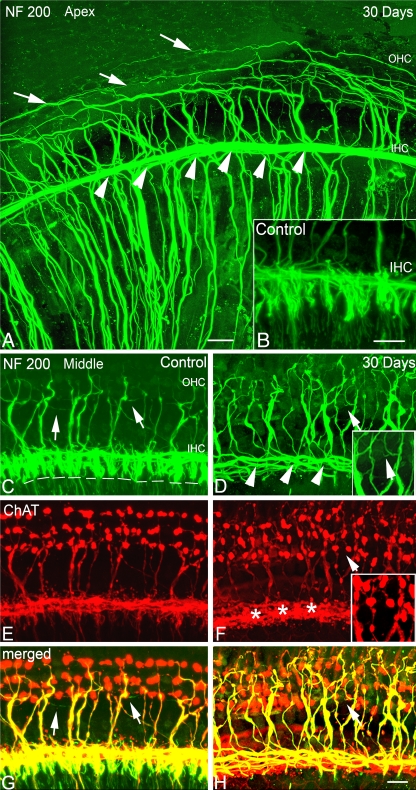
Cochlear afferent and efferent innervation patterns after ouabain treatment. A, B Loss of NF 200+ afferent fibers innervating IHCs (arrowheads) in the apical turn of a mouse at 30 days post-treatment. Surface preparation from the apical turns of a mouse 30 days after treatment shows the absence of NF200+ afferent fibers innervating inner hair cells (IHC, arrowheads). Also shown is a control ear (insert in B). The absence of radial afferent fibers allows a clear view of inner spiral bundle including both efferent and afferent fibers projecting into the outer hair cell (OHC) region. Numerous external spiral fibers are seen tracking spirally into the OHC region, including long, thin type II afferent fibers (arrows). C, E, G NF 200+ afferent fibers innervating IHCs (arrowheads) in the middle turn of another control mouse. Surface preparation stained with NF 200 (green) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT, red). The dashed lines indicate the location of the habenula perforata where nerve processes of type I SGNs lose their myelin sheath prior to entering the organ of Corti. White arrows indicate the long, thin type II afferent fibers. D, F, H Loss of NF 200+/ChAT− afferent fibers innervating IHCs in the middle turn of another mouse at 30 days post-treatment. Radial NF200+ fibers under IHCs disappear (arrowheads), whereas small thin NF 200+/ChAT− afferent fibers are still occasionally seen in the OHC region (white arrow). The inserts are the enlarged images of areas marked by a white arrow. The staining patterns of ChAT+ efferent fiber in the treated ear innervating OHCs are similar to those seen in a control ear. Numerous ChAT+ clusters are seen beneath IHC areas (asterisk). Scale bar, 15 μm in A and B; 20 μm in H (applies to C–H).