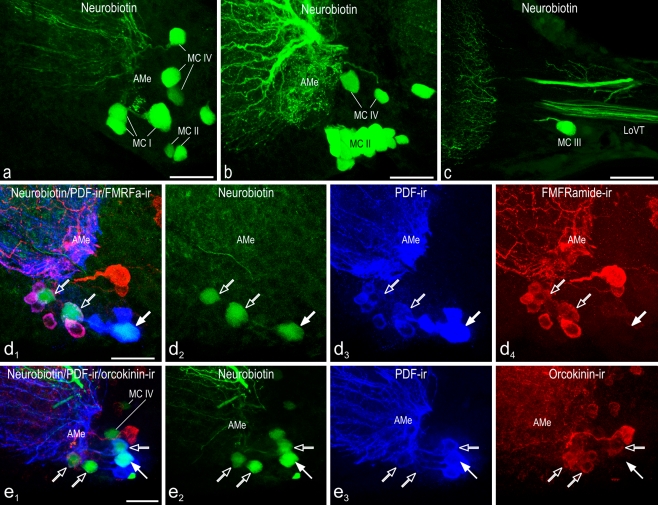
Fig. 5.
Confocal laser scan image projections of accessory medulla neurons backfilled from the contralateral optic lobe. Images are maximum projections from stacks of optical sections (green neurobiotin, blue PDF immunoreactivity, red FMRFamide or orcokinin immunoreactivity). Left in d, e Overlay images. Four groups of neurons of the accessory medulla (AMe) were labeled by neurobiotin backfill from the cut contralateral optic lobe (a-c). Contralaterally projecting medium-sized anterior PDFMe were additionally labeled by FMRFamide (d) or orcokinin (e) immunoreactivity. a Neurobiotin-filled neurons of the contralateral optic lobe projecting medulla cells group 1 (MC I), group 2 (MC II), and the newly discovered group 4 (MC IV). b The contralateral optic lobe projecting medulla cells group 2 (MC II) is the largest of the MC groups and comprises the VMNe group of the AMe. Group 4 (MC IV) neurons are also visible. c One neurobiotin-filled neuron of the group of the contralateral optic lobe projecting medulla cells group 3 (MC III) is immunostained (LoVT lobula valley tract). d 1-4 One large (filled arrows) and two medium-sized (open arrows) anterior PDFMe were backfilled from the optic lobe of the contralateral side. Medium-sized PDFMe could be easily recognized because of colocalized FMRFamide immunoreactivity only being present in these PDFMe. e 1-4 One large (filled arrow) and two medium-sized (open arrows) anterior PDFMe were backfilled from the optic lobe of the contralateral side. All medium-sized PDFMe showed colocalized orcokinin immunoreactivity (MC IV contralateral optic lobe projecting medulla cells group 4). Bars 50 μm