Abstract
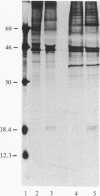
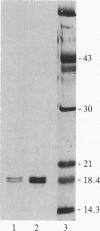
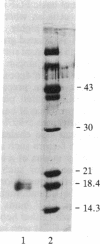
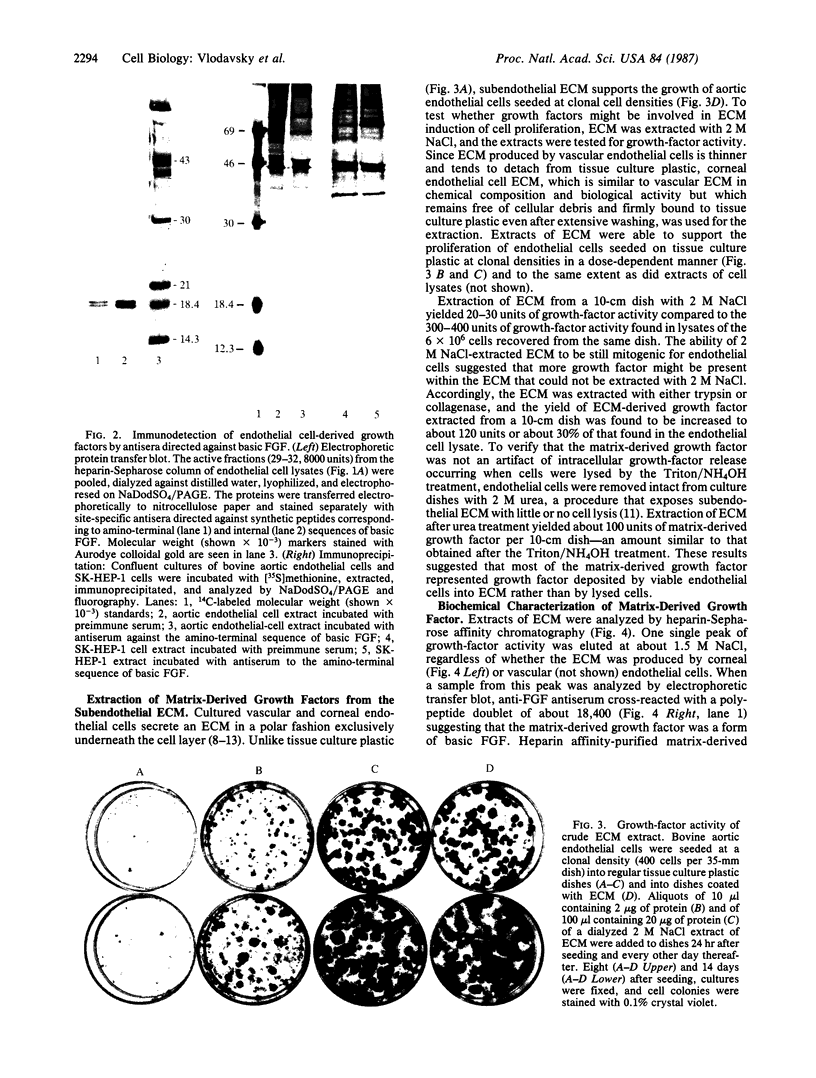
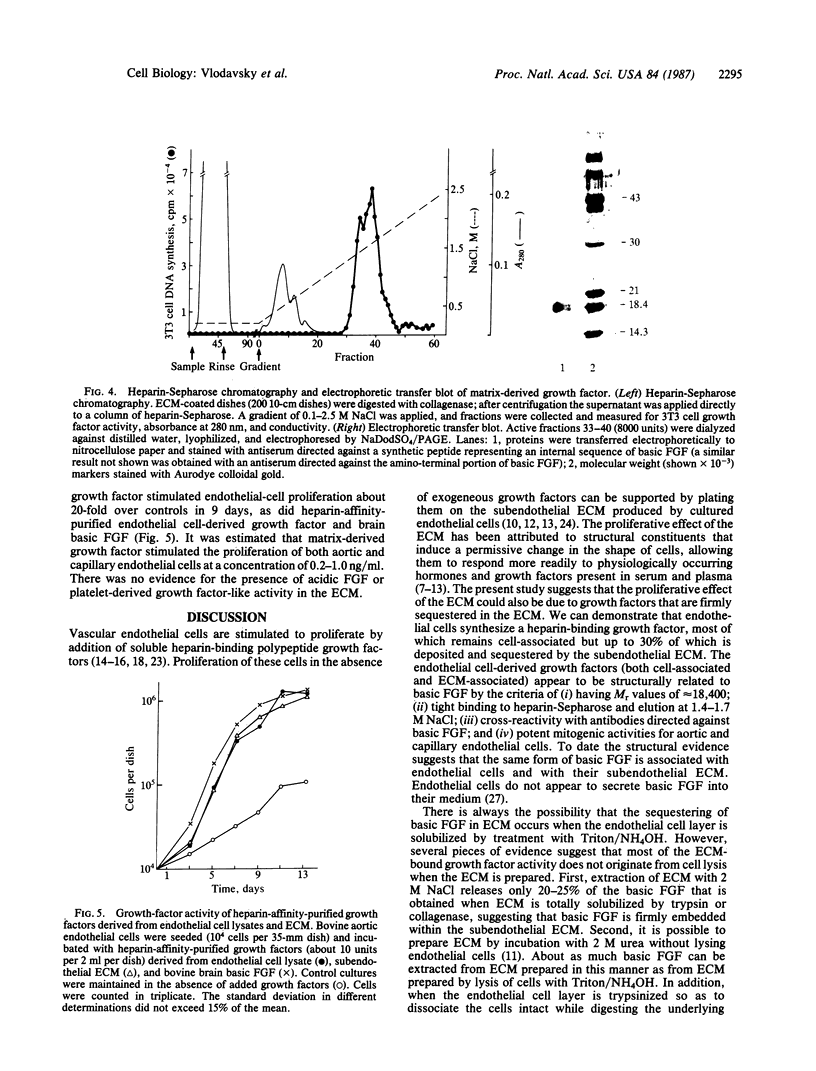
Bovine aortic and corneal endothelial cells synthesize a growth factor that remains mostly cell-associated but can also be extracted from the subendothelial extracellular matrix (ECM) deposited by these cells. The endothelial cell-derived growth factors extracted from cell lysates and from the extracellular matrix appear to be structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor by the criteria that they bind to heparin-Sepharose and are eluted at 1.4-1.6 M NaCl, have a molecular weight of about 18,400, cross-react with anti-basic fibroblast growth factor antibodies when analyzed by electrophoretic blotting and immunoprecipitation, and are potent mitogens for bovine aortic and capillary endothelial cells. It is suggested that endothelium can store growth factors capable of autocrine growth promotion in two ways: by sequestering growth factor within the cell and by incorporating it into the underlying extracellular matrix.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman R., Alon Y., Doljanski F., Fuks Z., Vlodavsky I. Cell interaction with the extracellular matrices produced by endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jun;158(2):461–476. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman R., Fuks Z., Ovadia H., Vlodavsky I. Differential structural requirements for the induction of cell attachment, proliferation and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Mar;157(1):181–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J. Heparin protects basic and acidic FGF from inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):475–484. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Delgado D., Vlodavsky I. Permissive effect of the extracellular matrix on cell proliferation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Gonzalez R., Fujii D. K. Are factors originating from serum, plasma, or cultured cells involved in the growth-promoting effect of the extracellular matrix produced by cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells? J Cell Physiol. 1983 Feb;114(2):191–202. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Birdwell C. R. Determination of cellular shape by the extracellular matrix and its correlation with the control of cellular growth. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4155–4171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ill C. Extracellular matrix and control of proliferation of vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1351–1364. doi: 10.1172/JCI109799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Mescher A. L., Birdwell C. R. Stimulation of corneal endothelial cell proliferations in vitro by fibroblast and epidermal growth factors. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jul;25(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenburg G., Gospodarowicz D. Inactivation of a basement membrane component responsible for cell proliferation but not for cell attachment. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jul;140(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobstein C. Mechanisms of organogenetic tissue interaction. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1967 Sep;26:279–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Smith J. A. Human tumor cells synthesize an endothelial cell growth factor that is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Vogel K. G., Nicolson G. L. Solubilization and degradation of subendothelial matrix glycoproteins and proteoglycans by metastatic tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2678–2686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Shing Y., D'Amore P., Jacobs J., Klagsbrun M. Purification and characterization of heparin-binding endothelial cell growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1924–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D. S., Liotta L. A., Kidwell W. R. Differential response to growth factor by rat mammary epithelium plated on different collagen substrata in serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Kenney J., Kowalski W. J., Friesel R., Mehlman T., Maciag T. Interaction of endothelial cell growth factor with heparin: characterization by receptor and antibody recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6138–6142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z., Bar-Ner M., Ariav Y., Schirrmacher V. Lymphoma cell-mediated degradation of sulfated proteoglycans in the subendothelial extracellular matrix: relationship to tumor cell metastasis. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2704–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Lui G. M., Gospodarowicz D. Morphological appearance, growth behavior and migratory activity of human tumor cells maintained on extracellular matrix versus plastic. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSELLS N. K. SUBSTRATE AND NUTRIENT EFFECTS UPON EPIDERMAL BASAL CELL ORIENTATION AND PROLIFERATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:252–259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]