Fig. 3.
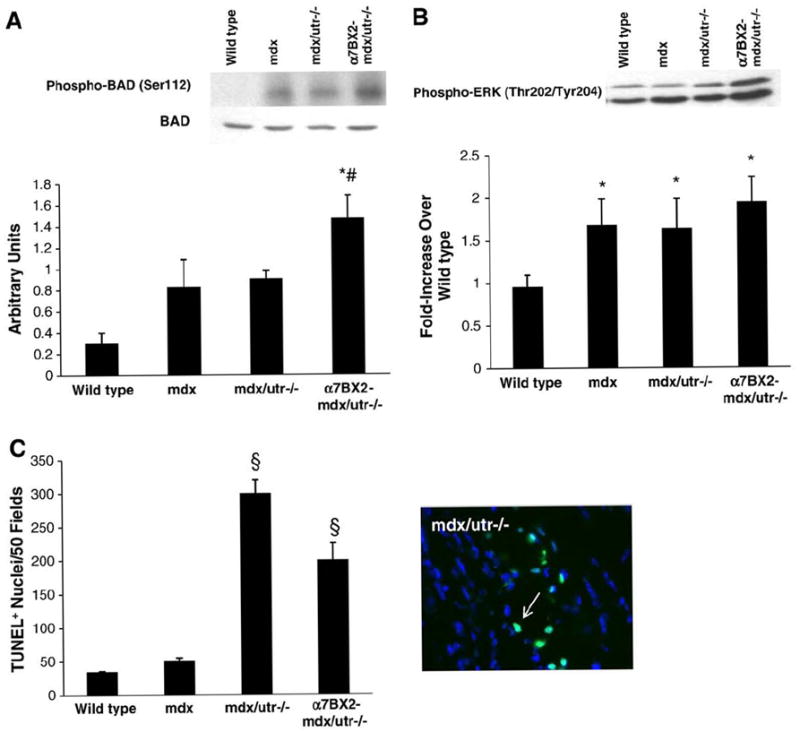
Phosphorylation of BAD and ERK is increased and apoptosis is inhibited in α7BX2-mdx/utr−/− mice. (A) BAD phosphorylation (Ser112) was examined in 5 week-old wild type, mdx, mdx/utr−/−, and α7BX2-mdx/utr−/− mice (n=4–8/grp) and reported as a percentage of an internal control sample. BAD phosphorylation was significantly increased only in α7BX2-mdx/utr−/− compared to wild type mice. Total BAD levels were unchanged (not shown). (B) ERK is an upstream regulator of BAD Ser112 phosphorylation. ERK phosphorylation was increased in all groups (n=4–8/grp). (C) TUNEL+ nuclei were counted as an indication of apoptosis in skeletal muscle of 5 week-old wild type, mdx, mdx/utr−/−, and α7BX2-mdx/utr−/− mice (n=4–7/grp). A representative image of TUNEL staining is shown. Apoptosis was significantly increased in mdx/utr−/− mice compared to wild type and mdx, and apoptosis was suppressed in dystrophic mice expressing the α7 integrin transgene. *=vs. wild type, #=vs. mdx, and §=vs. all groups (P<0.05).
