Fig. 6.
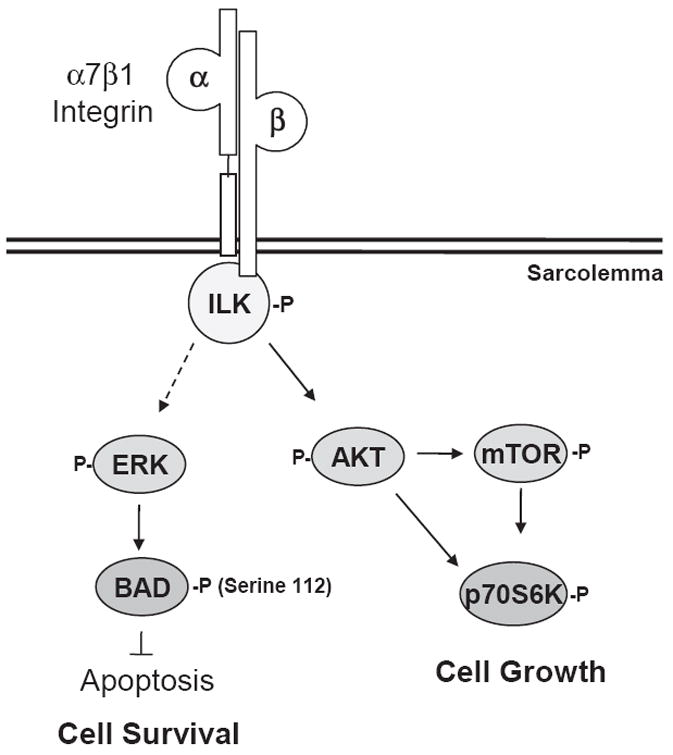
Signaling pathways by which the α7 integrin decreases pathology in dystrophic mice. The α7 integrin–ILK complex is activated in response to extracellular matrix attachment, resulting in phosphorylation of AKT and p70S6K in an mTOR-dependent or independent manner, resulting in increased muscle growth. The α7–ILK complex may also stimulate phosphorylation of BAD on Ser112 (via ERK), suppressing the pro-apoptotic actions of BAD and enhancing cell survival.
