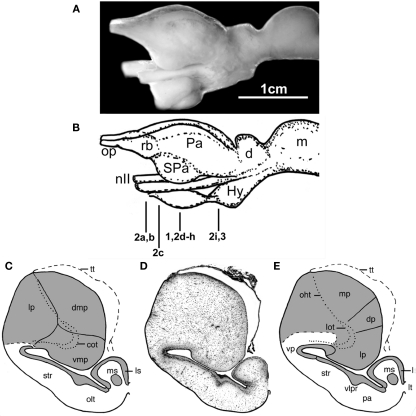
Figure 1.
The forebrain and midbrain the Comoran coelacanth. (A) Photograph of a lateral view of the forebrain and midbrain. (B) Line drawing of the lateral view, indicating the levels of the transverse section in Figures 1–3. (C) Line drawing of a transverse section through one telencephalic hemisphere showing the boundaries of cell groups interpreted by Nieuwenhuys (1965) and Nieuwenhuys and Meek (1990). (D) A Nissl-stained section from the present study, showing the actual histology. (E) Line drawing indicating the boundaries of the cell groups as interpreted in the present study. Dotted lines in (C,E) indicate the lateral olfactory and olfactohabenular tracts. Short, heavy dashed lines indicate the subpallial–pallial boundary (C) or the boundary between the neuropil of the ventral pallium and the medial pallium (E). cot, Central olfactory tract; d, diencephalon; dmp, dorsomedial pallium; dp, dorsal pallium; Hy, hypothalamus; Hyp, hypophysis; lot, lateral olfactory tract; lp, lateral pallium; ls, lateral septum; lt, lamina terminalis; m, mesencephalon; mp, medial pallium; ms, medial septum; nII, optic nerve; oht, olfactohabenular tract; olt, olfactory tubercle; op, olfactory peduncle, Pa (in lateral view), pallium; pa (in transverse section), pallidum; rb, rostral body; SPa, subpallium; str, striatum; tt, telencephalic tela; vlpr, ventrolateral cellular prominence; vmp, ventromedial pallium; vp, ventral pallium.