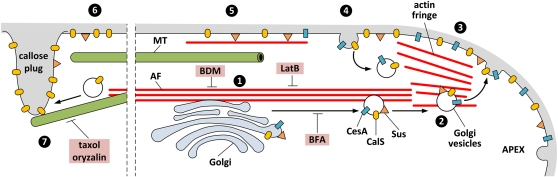
Figure 10.
Schematic drawing showing the current hypothesis about CalS/CesA insertion into the pollen tube plasma membrane. CalS and CesA are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (data not shown) and in Golgi bodies transported to the subapex along bundles of actin filaments (1), from where Golgi vesicles to which Sus also is associated (2) move to the apical plasma membrane where the vesicle membrane is inserted, including the enzymes (3). In the subapex, the excess of CalS and CesA is removed by endocytosis and may be eventually recycled (4). Accordingly, a smaller proportion of CalS and CesA persists in the tube (5), although new insertion of CesA make take place here. Sus might associate with cortical actin filaments, which are used to establish the correct spatial arrangement. Additional CalS, but not CesA, is inserted into the plasma membrane where a callose plug is formed (6), the localization of which is determined by microtubules (7). The targets of the inhibitors used are indicated. Objects are not drawn to scale. Dotted lines indicate that the distance between the apex and the first callose plug is larger than shown.