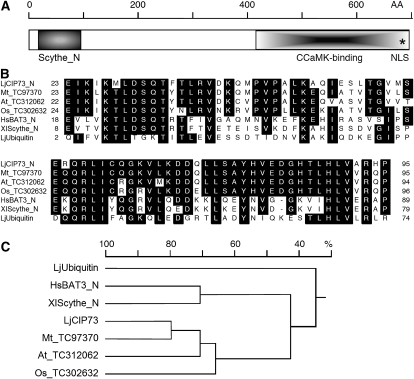
Figure 1.
CIP73 contains a Scythe_N ubiquitin-like domain and belongs to the large ubiquitin superfamily. A, Schematic illustration of the CIP73 protein. The deduced amino acid sequence of CIP73 contains 691 amino acid residues with a calculated molecular mass of approximately 73 kD. Notable features include the Scythe_N (Scythe is also known as BAT3) ubiquitin-like domain at the N terminus (21–93) and a putative NLS (686–689) shown by the asterisk. The CCaMK-binding region identified in the original Y2H screening (414–691) is in the CIP73 C-terminal region. B, Multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal ubiquitin-like domain of CIP73 and the homologous sequence from Medicago (TC97370), Arabidopsis (TC312062), rice (TC302632), human BAT3_N (NP_542433), Xenopus Scythe_N (NP_001080008), and L. japonicus ubiquitin (AW720576). The numbers on the left and right indicate the positions of amino acids. C, Homology tree of the N-terminal ubiquitin-like domain of CIP73 homologs, Scythe_N, and ubiquitin. The tree was constructed using the DNAMAN software (version 5.2.2; Lynnon Biosoft). Note that the N-terminal ubiquitin-like domain of CIP73 is more closely related to the animal Scythe_N domain than to LjUbiquitin.