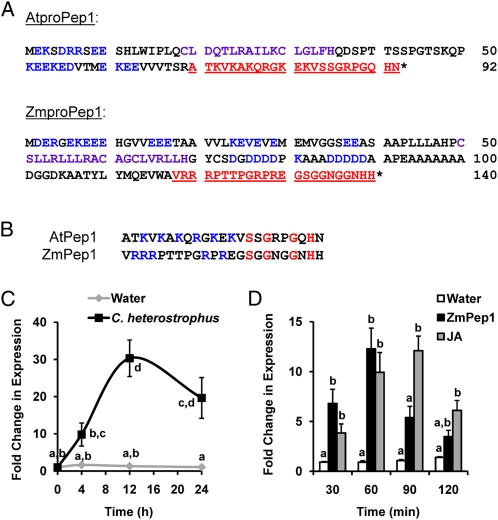
Figure 1.
Comparison of the proteins encoded by the AtPROPEP1 and ZmPROPEP1 genes. A, Conserved precursor motifs are the EKE motif (blue), amphipathic helix motif (purple), and bioactive elicitor peptide (red, underlined). B, Comparison of conserved characteristics within the active AtPep1 and ZmPep1 peptides. Basic residues are blue, and identical amino acids are red. C, Average ± se (n = 3) induced ZmPROPEP1 gene expression in leaves by the fungal pathogen C. heterostrophus. D, Average ± se (n = 3) induced expression of the ZmPROPEP1 precursor gene in response to treatment of intact leaves with ZmPep1 or JA. In C, different letters (a–d) represent significant differences within the plot. In D, different letters (a and b) represent significant differences within each time point (all ANOVAs, P < 0.005; Tukey test corrections for multiple comparisons, P < 0.05).