Figure 4.
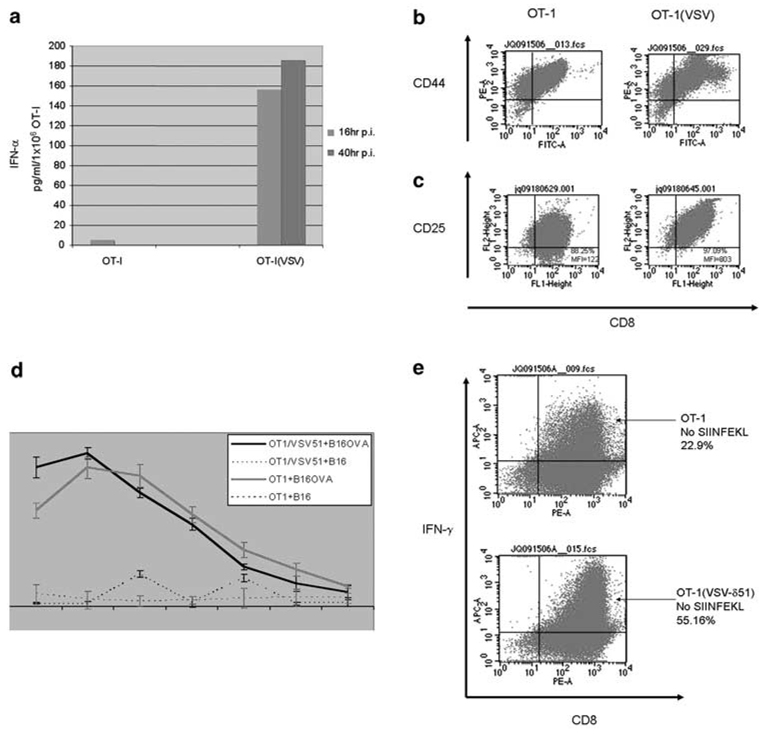
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-δ51 loading activates OT-I. (a) A total of 1 × 106 OT-I, or VSV-δ51-loaded OT1 (OT-I(VSV)), were plated in six-well plates. Culture supernatants were harvested at 16 and 40 h postinfection (p.i.), and were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for interferon (IFN)-α. (b, c) OT-I cells were loaded at an MOI of 1 with VSV-δ51 or left unloaded. After 24 h, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for expression the T-cell activation markers CD44 (b) or CD25 (c) along with CD8. (d) Three-day-activated OT-I, or OT-I cells loaded with VSV-δ51 (MOI 1) were used as effectors against B16 or B16ova targets loaded with Cr51. OT-I cells (effectors) were incubated for only short periods of time with their targets (B16 or B16ova) at the ratios shown, supernatants were harvested and analyzed for Cr51 release. Levels of lysis were relatively low in these assays because of the short period of time over which the assay needed to be conducted to exclude tumor cell lysis as a result of infection by VSV-δ51 released from the loaded OT-I T cells. Thus, control experiments demonstrated that cytotoxicity to B16 or B16ova tumor cells as a result of infection with VSV-δ51 is only significant after 6 h of virus incubation (not shown). Data shown are representative of three separate experiments; bars, s.d. *P<0.05 (VSV/OT1+B16 versus OT1+B16). (e) Three-day activated OT-I cells were loaded at an MOI of 1 with VSV-δ51 or left unloaded. The OT-I cells were grown for a further 24 h in the absence of added SIINFEKL peptide and were analyzed by flow cytometry for intracellular expression of IFN-γ along with CD8.