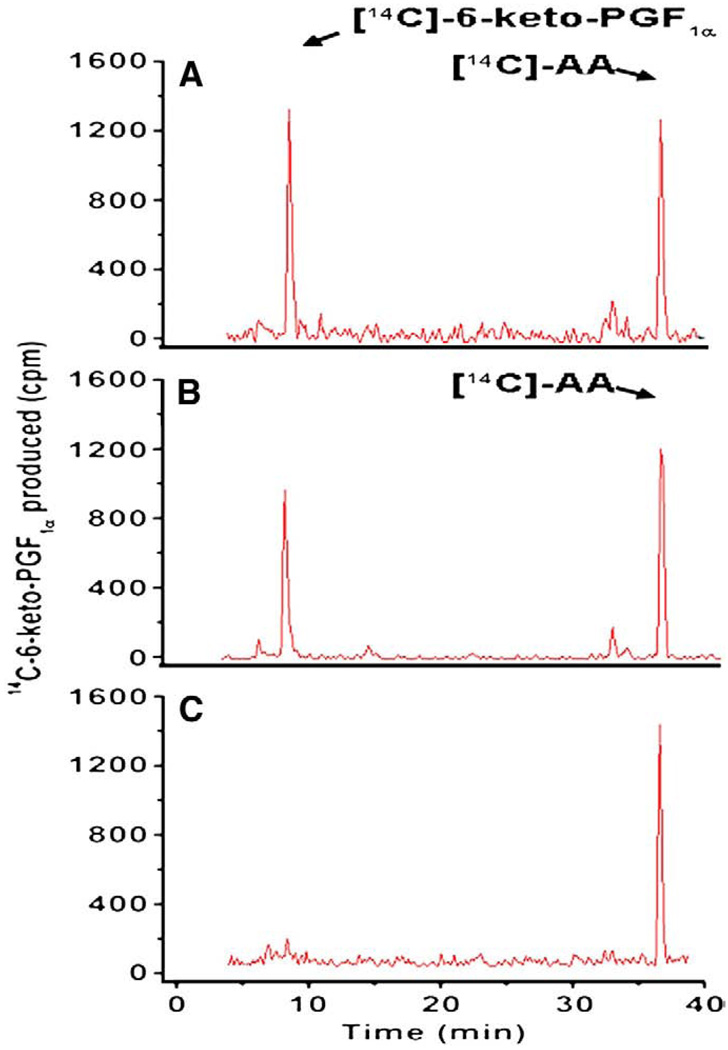
Fig. 2.
Determination of the triple catalytic reactions of COX coupled to PGIS in biosynthesis of PGI2. The COS-7 cells (~0.1×106) transfected with the recombinant cDNA(s) of COX-1 and PGIS (A), or COX-2 and PGIS (B) were washed three times, suspended in 0.01 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, containing 0.15% NaCl (PBS) and then incubated with [14C]-AA (10 µM) in a total volume of 30 µL. After 5 min, the reaction was terminated by the addition of 50 µL of 0.1% acetic acid containing 35% acetonitrile (buffer A), and centrifuged at 17,000 ×g for 5 min. The supernatant was separated by HPLC on a C18 column (4.5 × 250 mm) using buffer A with a gradient of 35–100% acetonitrile. The [14C]-AA metabolites were determined by a liquid scintillation analyzer built in the HPLC system. The retention times of [14C]-6-keto-PGF1α and [14C]-AA were calibrated by standards under the same conditions. The amounts of produced 6-keto-PGF1α represented the amounts of the produced PGI2. The produced [14C]-6-keto-PGF1α was quantitated based on the equation: 100 cpm is equal to approximately 0.5 pg of [14C]-6-keto-PGF1α. The untransfected COS-7 cells were used as a negative control (C).