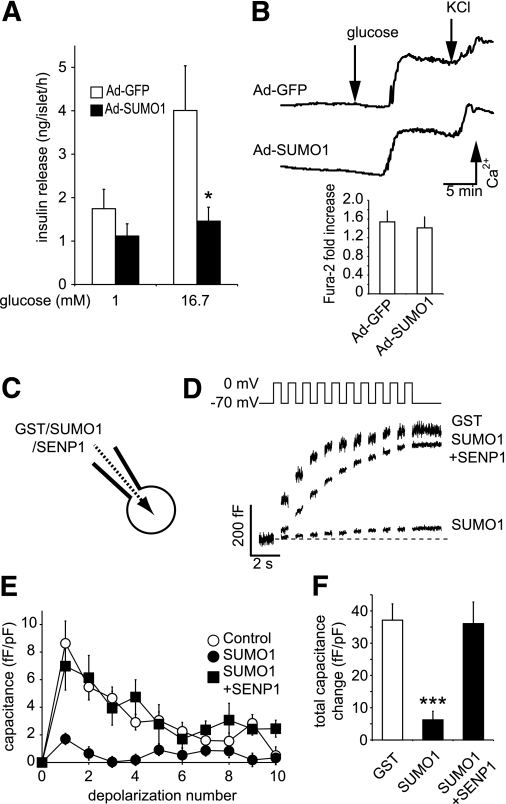
FIG. 1.
SUMOylation impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by acute inhibition of β-cell exocytosis. A: Insulin secretion from isolated mouse islets expressing either GFP alone (Ad-GFP, □) or SUMO1 (Ad-SUMO1, ■). B: Intracellular Ca2+ responses to glucose and KCl in these islets by ratiometric imaging of Fura-2-AM. The glucose-stimulated increase in the Fura-2 ratio is shown at the bottom. C: Single-cell experiments were performed on β-cells by whole-cell patch clamp, allowing the direct and acute intracellular dialysis of a control peptide (GST), SUMO1, or SENP1. D: Mouse β-cell exocytosis, measured as an increase in capacitance (cell size) during a train of ten 500-ms depolarizations (top), after ~4 min of dialysis with GST, SUMO1, or SUMO1 + SENP1. E: Average capacitance response to each step-wise depolarization. F: The total capacitance response over the train of depolarizations. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 vs. controls.