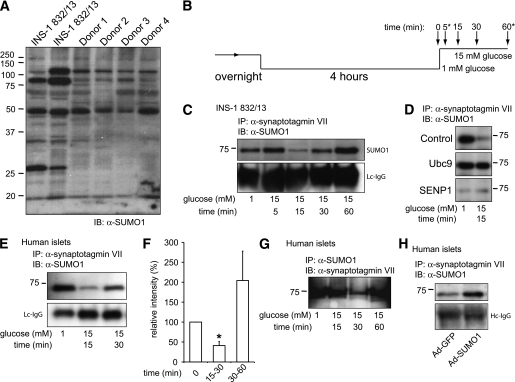
FIG. 5.
SUMO1 associates with the exocytotic Ca2+ sensor synaptotagmin VII in a glucose-dependent manner. A: SUMOylation profile of whole-cell lysates from INS-1 832/13 cells and four human donors showing numerous SUMOylated proteins. B: INS-1 832/13 cells and human islets were cultured overnight, preincubated at 1 mmol/L glucose for 4 h, and stimulated with 15 mmol/L glucose for varying times, as indicated. At some time points (*) lysates were not always collected. C: Immunoprecipitation of synaptotagmin VII from INS-1 832/13 cells collected at time points following glucose-stimulation indicated in B, followed by blotting for SUMO1. Light-chain (Lc) or heavy chain (Hc) IgG is shown as a loading control. D: Same as in C, collected at time = 0 and 15 min following glucose stimulation. The interaction between SUMO1 and synaptotagmin VII in INS-1 832/13 cells is increased by the SUMO-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 and lost upon expression of the SUMO protease SENP1, in comparison with cells transfected with control vector. Ubc9 prevents, whereas SENP1 mimics, the glucose-dependent disruption of the interaction. E: Same as in C but with human islets. F: Densitometry demonstrates a >50% reduction in SUMO1 coimmunoprecipitation at 15 min following glucose stimulation of human islets. G: As in D but with SUMO1 immunoprecipitation followed by blotting for synaptotagmin VII. H: As in D, after infection with Ad-GFP or Ad-SUMO1, demonstrating that increasing SUMO1 expression enhances the interaction with synaptotagmin VII. *P <0.05 vs. time = 0. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)