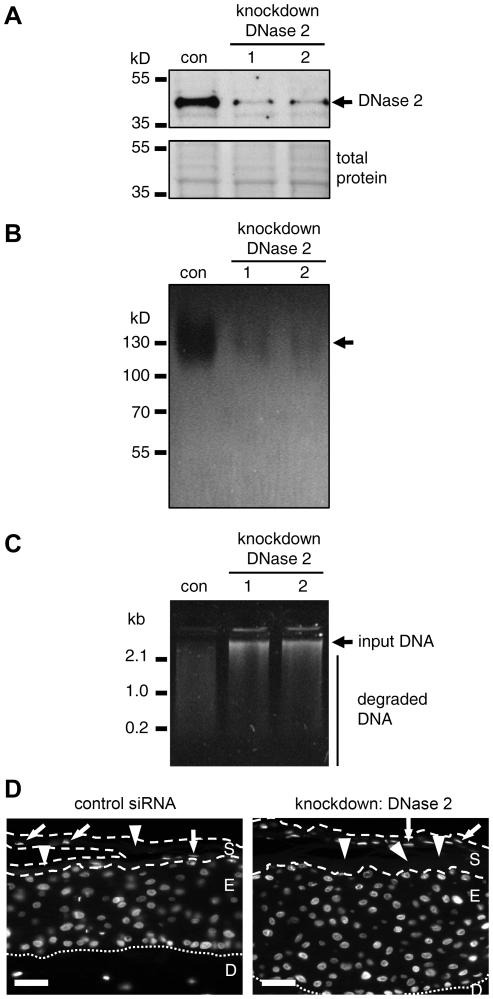
Figure 4. siRNA-mediated knockdown of DNase 2 reduces the main acid DNase activity of a human skin equivalent.
The expression of DNase 2 was knocked down by specific short interfering RNAs (siRNA1, siRNA2) in human skin models in vitro. (A) The skin equivalents were lysed and subjected to Western blot analysis using an antibody specific for DNase 2 (top panel). Equal loading was confirmed by Ponceau staining of the same membrane (bottom panel). con, control siRNA. (B) DNase zymography of lysates from skin equivalents. (C) DNase activity of lysates from skin equivalents was determined at pH 4.8. Lysates were incubated with Lambda DNA. DNA degradation was visualized by gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. kb, kilo-basepairs. (D) Labeling of nuclear DNA with Hoechst 33258 in thin sections of skin equivalents. Fluorescent labeling of DNA is shown in white. The borders of the stratum corneum are marked by discontinuous lines and the border of the epidermis and dermis is marked by dotted line. Arrows point to nuclear remnants occurring sporadically in the stratum corneum. Arrowheads point to stratum corneum free of nuclear remnants. S, stratum corneum; E, epidermis; D, dermis; Scale bars, 40 µm.