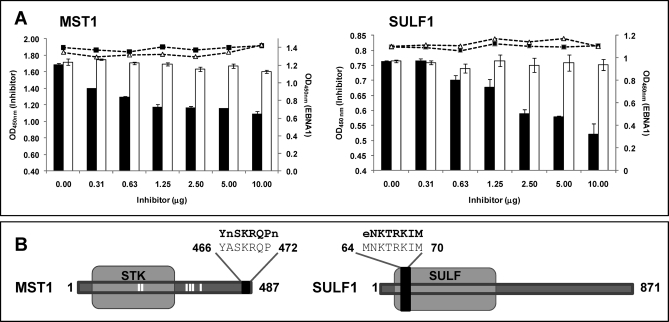
Fig. 3.
Competition analysis between phage-peptides and homologous proteins. A, A competition ELISA was performed between phages displaying peptides with homology to SULF1 and MST1 and the full-length proteins. GST was used as negative control. Increasing amounts of the recombinant proteins were pre-incubated with the sera and then tested for antibody binding to the phage (vertical bars: black, recombinant protein; white, GST). In the scatter plot, the IgG binding to EBNA1 of the same sera, pre-incubated with increased amounts of recombinant proteins is represented. EBNA 1 was used as a control to demonstrate that the inhibition was protein-specific and no bias was introduced in the experiment (black squares, recombinant protein; white triangles, GST). The Optical Density (OD) at 450 nm of both assays is represented in the figure. Error bars represent standard deviation of three separate experiments. B, Localization of the peptides with homology to SULF1 and MST1 in the full length proteins. Phage-displayed peptide is shown as a black box. White bars correspond to potential phosphorylation sites. Amino acids that were different between the phage-peptide and the wild-type protein are represented in small letter.