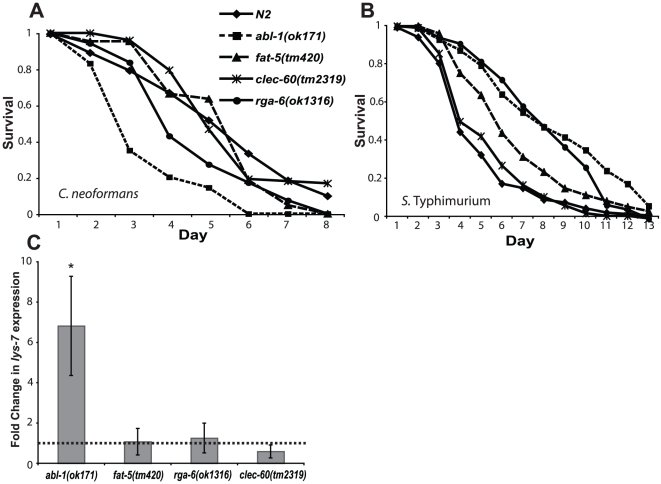
Figure 2. abl-1 and rga-6 mutant animals phenocopy lys-7 susceptibility patterns.
Knockout C. elegans strains for the four genes which were identified by a microarray to be up-regulated in the lys-7 mutant background were assayed for survival upon infection with both C. neoformans and S. Typhimurium. The survival of abl-1(ok171) and rga-6(ok1316) animals was significantly lower than wild type animals upon C. neoformans infection (A), p<0.0001 and p<0.01 respectively. The remaining animals were unchanged from wild type survival, p>0.2, [N2 n = 186; abl-1(ok171) n = 130; rga-6(ok1316) n = 192; fat-5(ok460) n = 100; clec-60(tm2319) n = 110]. abl-1(ok171), rga-6(ok1316) and fat-5(tm420), but not clec-60(tm2319), animals exhibited enhanced resistance to S. Typhimurium (B), p<0.0001 in each case, [N2 n = 170; abl-1(ok171) n = 222; rga-6(ok1316) n = 100; fat-5(ok460) n = 162; clec-60(tm2319) n = 125]. (C) abl-1 mutant animals up-regulate lys-7 expression (average induction of 6.8 fold; p<0.05), whereas lys-7 expression is unchanged from wild type in the remaining mutant backgrounds. Data represent the mean expression of three independent experiments, ± S.E.M.