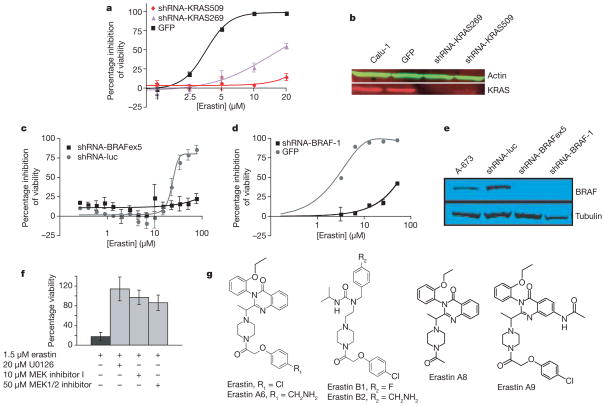
Figure 2. Erastin lethality is dependent on the RAS–RAF–MEK pathway.
a, Calu-1 cells infected with lentivirus containing shRNAs targeting KRAS were resistant to erastin-induced lethality as quantified by way of comparison with green fluorescent protein (GFP) control in Trypan blue exclusion assay. Sequences of shRNAs are indicated by starting nucleotide in the KRAS mRNA coding sequence. b, KRAS knockdown was confirmed by western blot analysis. c, d, A-673 cells were infected with lentivirus expressing indicated shRNAs or a control GFP plasmid. Cells were treated with erastin for 24 h; percentage inhibition of viability (y axis) was measured using c, Alamar blue and d, Trypan blue. Luc, luciferase; BRAFex5, exon 5 of BRAF transcript. e, BRAF knockdown was confirmed by western blot analysis. f, 48 h treatment with MEK inhibitors (U0126, Sigma; MEK inhibitor 1, Calbiochem; MEK1/2 inhibitor, Calbiochem) prevents erastin-induced lethality in BJ-TERT/LT/ST/RASV12 cells; percentage viability (y axis) was determined using Trypan blue. g, Structures of erastin and related analogues. All error bars in Fig. 2 represent one standard deviation; n =2 or 3.